Fig. 2.
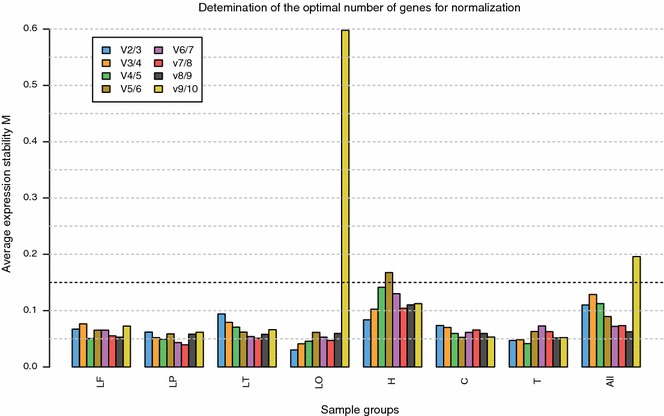
Determination of the optimum number of reference genes for normalisation of RT-qPCR data. The GeNorm program calculates the normalisation factor (NF) for a given number of genes (n) and defines the pairwise variation (V) between the sequential normalisation factors NFn and NFn+1. For example V2/3 represents the variation in NFs using the two versus three most stable control genes. A low V value indicates little variation, implying that adding the extra gene has no significant effect. Pairwise variation (V) < 0.15 is regarded to result in valid normalisation. Using this cut-off value all evaluated brain regions require only two reference genes for accurate normalisation. Results are based on analysis of 7 brain areas of 7 dogs each: LF lobus frontalis, LP lobus parietalis, LT lobus temporalis, LO lobus occipitalis, H hippocampus, C cerebellum, T thalamus, All average of all areas
