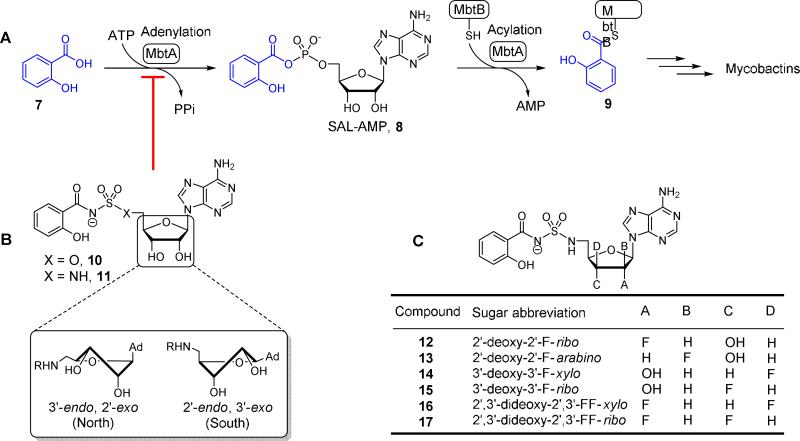
Figure 2.
Mycobactin biosynthesis and inhibition. (A) The biosynthesis of mycobactins in M. tuberculosis is initiated by MbtA that catalyzes two partial reactions at the same active site. In the first half-reaction MbtA condenses salicylic acid (7) with ATP to form the reactive mixed anhydride SAL-AMP (8). In the second half-reaction MbtA transfers the salicyl moiety onto MbtB, another protein in the biochemical pathway, to afford 9 that is ultimately elaborated to the mycobactins. The initial biosynthetic step of other aryl-capped siderophores is performed by homologous aryl acid adenylation enzymes (AAAEs). (B) The inhibitors Sal-AMS 10 and its sulfamide isostere 11 mimic the acyl-adenylate intermediate 8, thereby blocking siderophore biosynthesis. The sugar can adopt the Northern (C3′-endo pucker) or Southern (C2′-endo pucker) conformation as depicted. (C) Fluorinated sugar analogs described in this study.