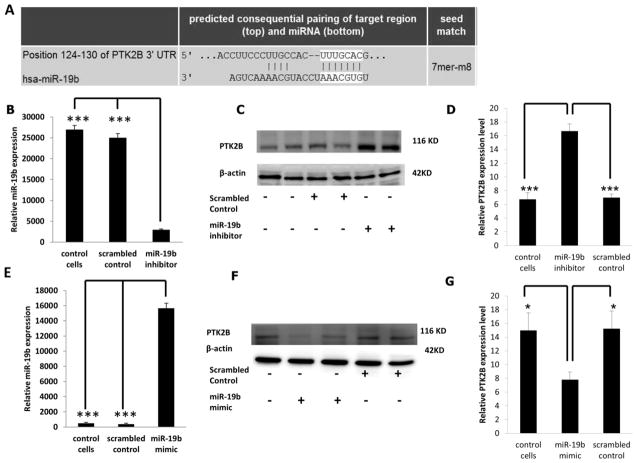
Figure 1. PTK2B expression following knockdown or overexpression of miR-19b.
(A) Predicted binding of miR-19b to the 3′ UTR of PTK2B as assessed by Target Scan (http://www.targetscan.org/). (B) Knockdown of miR-19b was carried out by transfecting miR-19b inhibitor or scrambled miRNA inhibitor (control) in HCT116 cells. Forty-eight h following transfection, miR-19b expression was measured by qRT-PCR. (C) PTK2B protein levels were measured by Western blotting after miR-19b knockdown and β-actin was used as a loading control as described in the Materials and Methods. (D) Quantification of PTK2B levels in control (no transfection), scrambled control or miR-19b knockdown samples from immunoblot images. (E) Overexpression of miR-19b was carried out by transfecting miR-19b mimic or scrambled miRNA mimic control and 24 h later, miR-19b expression was measured by qRT-PCR. (F) PTK2B protein levels were measured by western blotting following miR-19b overexpression, and β-actin was used as a loading control. (G) Quantification of PTK2B levels in control (no transfection), scrambled control or miR-19b overexpressed samples from immunoblot images. Data represent means ± S.E. from six-eight replicate values obtained from three separate experiments. Significant differences between groups are indicated as ***P < 0.001, and *P < 0.05.