Table 1.
Physicochemical and toxicological information of allyl chloride∗
| Chemical name | Allyl chloride |
| CAS No. | 107-05-1 |
| Synonyms | 1-Chloro-2-propene 1-Propene, 3-chloro- 2-Propenyl chloride 3-Chloropropene Chlorallylene p-Aminopropiofenon 1-Chloropropylene |
| Molecular formula | C3H5Cl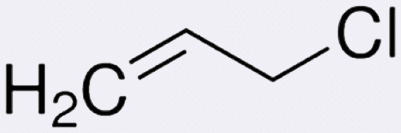
|
| Molecular weight | 76.5 |
| Melting point | −135°C |
| Forms | Colorless liquid |
| Partition coefficient | 2.1 |
| Boiling point | 45°C |
| Water solubility | 0.337 g/100 mL at 25°C |
| Stability & reactivity | Chemical stability: stable under recommended storage conditions Conditions to avoid: heat, flames, & sparks; temperature extremes; & direct sunlight Materials to avoid: oxidizing agents, boron trifluoride, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, & strong oxidizing agents |
| Toxicity | Target organs: liver, respiratory system Human LCLo inhalation, 3000 ppm Mouse LC50 inhalation, 11500 mg/m3/2H Mouse LD50 intraperitoneal, 155 mg/kg Mouse LD50 oral, 425 mg/kg Rabbit LCLo inhalation, 22500 mg/m3/2 h Rabbit LD50 skin, 2066 mg/kg Rat LC50 inhalation, 11 gm/m3/2H Rat LD50 oral, 460 mg/kg Guinea pig LC50 inhalation, 5800 mg/m3/2 h Allyl chloride is classified as Group 3 (i.e., not classifiable regarding its carcinogenicity to humans) in IARC, A3 in ACGIH, & Carc 2 in EU-CLP |
| GHS classification | Flammable liquids (Category 2) Acute toxicity, oral (Category 4) Acute toxicity, inhalation (Category 3) Skin irritation (Category 2) Eye irritation (Category 2) Carcinogenicity (Category 2) in MoEL of Korea & the IARC Group 3 Germ cell mutagenicity (Category 2) in the MoEL of Korea Specific target organ toxicity-single exposure (Category 3), respiratory system |
ACGIH, American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists; CAS, Chemical Abstract Service; EU-CLP, European Union Classification, Labelling, and Packaging; GHS, Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals; IARC, International Agency for Research on Cancer; LC50, median lethal concentration; LCLo, lowest lethal concentration; MoEL, Ministry of Employment and Labor.
The information is mostly obtained from searching ChemIDplus Advanced, U.S. National Library of Medicine (Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD; http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/107-05-1), and Material Safety Data Sheet in KOSHANET (Ulsan, Korea; http://msds.kosha.or.kr/kcic/msdsdetail.do). The searches were conducted using keywords, the chemical name, and/or the CAS number.
