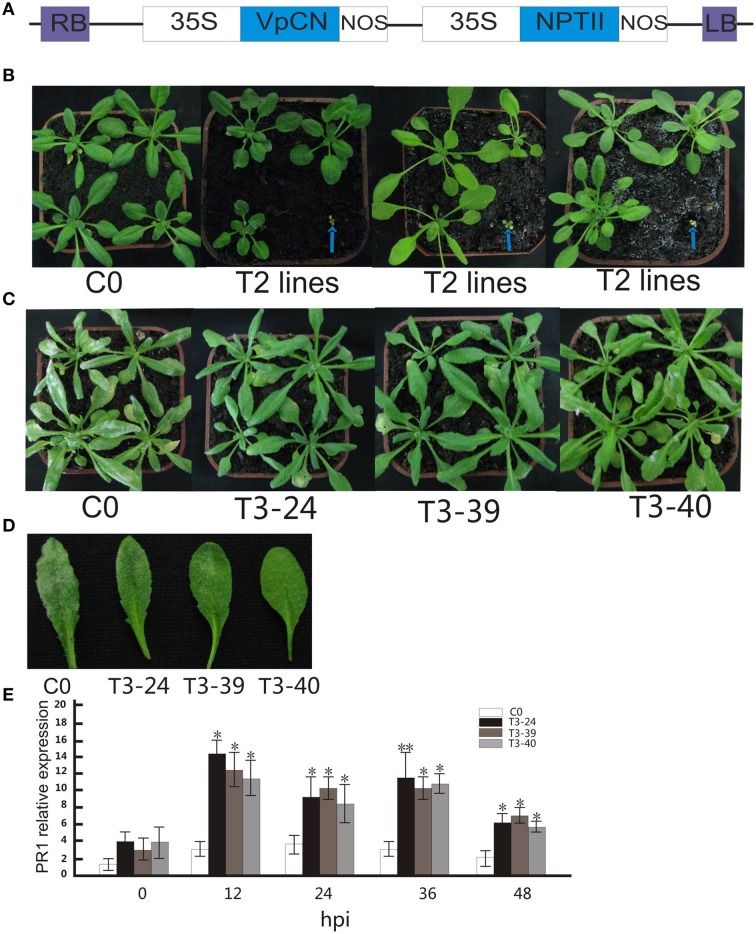
Figure 2.
Generation of CaMV 35S promoter-VpCN constructs used for transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana, morphology of wild type and transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants, with transgenic plants showing enhanced disease resistance to G. cichoracearum after ectopic expression of VpCN. (A) Structure of the CaMV 35S promoter-VpCN ectopic expression construct. LB, left border; RB, right border; 35S, CaMV 35S promoter; NOS, terminator; NPT II, aminoglycoside-3′- phosphotransferase. (B) Indicate T2 transgenic plants displayed either normal phenotypes or dwarfism. Blue arrows indicate the dwarf phenotype in 4 week old plants. (C) Transgenic A. thaliana leaves developed fungal spores 8 dpi with G. cichoracearum. (D) Disease symptoms developed on the leaves of transgenic lines and wild type plants 8 dpi with G. cichoracearum. (E) A. thaliana PR1 transcript levels in T3 lines and wild-type after inoculation with G. cichoracearum. Total RNA was extracted from A. thaliana leaves 0, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h post-inoculation (hpi) with G. Cichoracearum. The experiment encompass three independent biological replicates, for each biological replicate six rosette leaves were harvested from three plant and three technical replicates were performed. Data represent means of three biological replicates ±SE, asterisksin indicate statistical significance in comparison with WT (Student's t-test, significance levels of *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 are indicated).