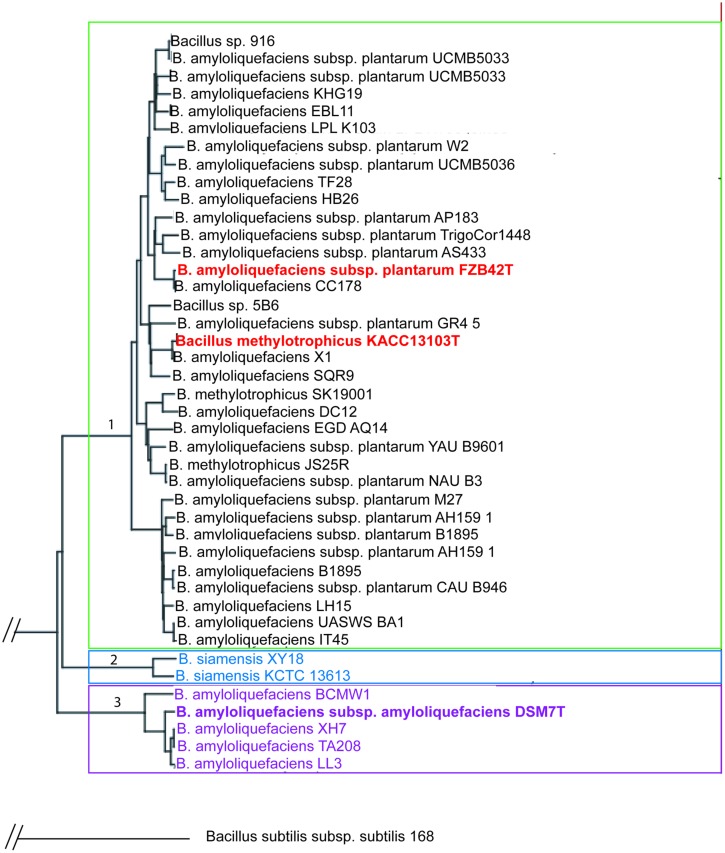
FIGURE 1.
Phylogenetic tree of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens chromosomes currently available in public databases. Based on the core genome of 2104 CDS the divergence of the plant-associated bacteria (B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum) and B. siamensis and B. amyloliquefaciens subsp. amyloliquefaciens was quantified with FZB42T employed as reference to construct the tree according to Blom et al. (2009). Every set of orthologous genes found in all genomes was separately aligned using the multiple alignment tool MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004). The alignments were concatenated to one huge multiple alignment. A distance matrix was calculated from this alignment and finally a phylogenetic tree was constructed based on this distance matrix using the Neighbor-Joining method. The two latter methods are used in the PHYLIP implementations by Felsenstein (http://evolution.genetics.washington.edu/phylip.html). The Neighbor-Joining method was chosen as it is a heuristic approach with a very good computational efficiency, making it well suited for large datasets resulting from the core genome based tree construction.