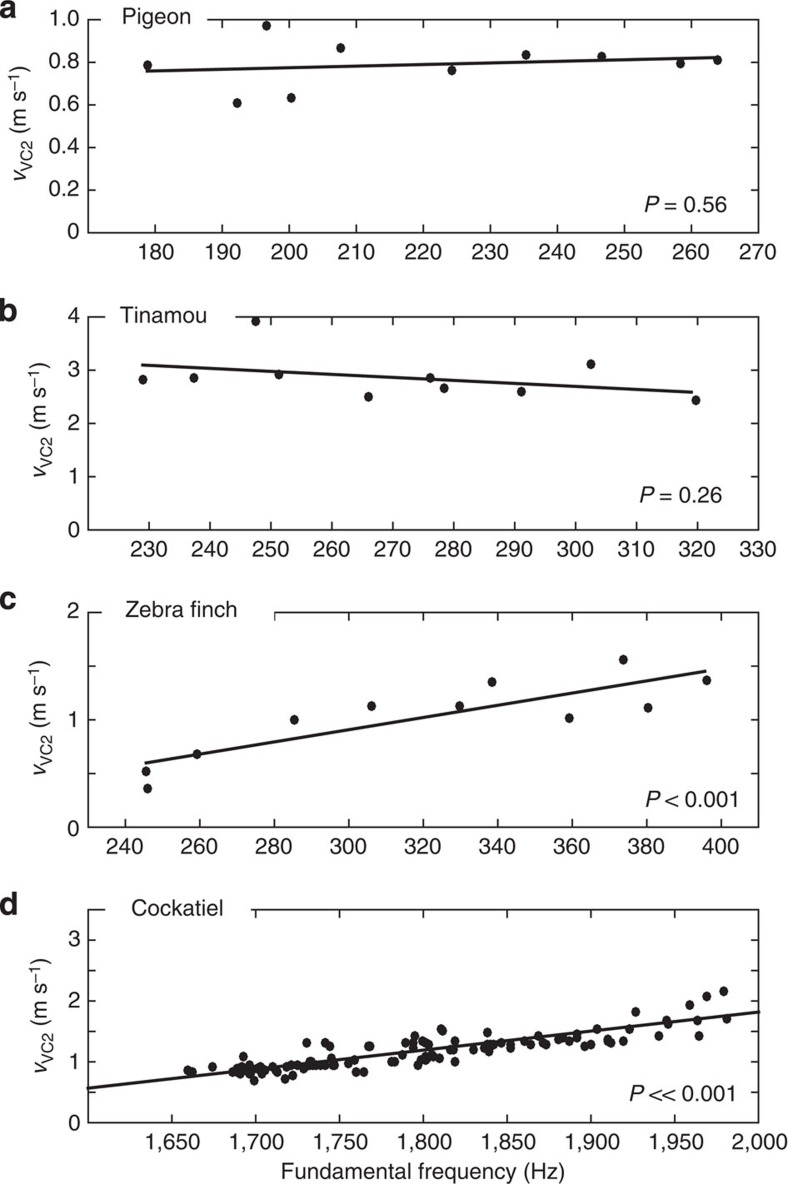
Figure 4. The caudo-cranial tissue wave is present across a range of fundamental frequencies.
Magnitude of the caudo-cranial component (vVC2) of the travelling tissue-wave's velocity in (a) pigeon and (b) tinamou, (c) zebra finch and (d) cockatiel. The positive velocity values indicate that the wave travelled from caudal to cranial. Wave speed remained constant with F0 in pigeon and tinamou (Linear regression, P=0.56 (n=10) and P=0.26 (n=10), respectively), but increased significantly with F0 in zebra finch and cockatiel (linear regression, P<0.001 (n=11) and P<<0.001 (n=118), respectively).