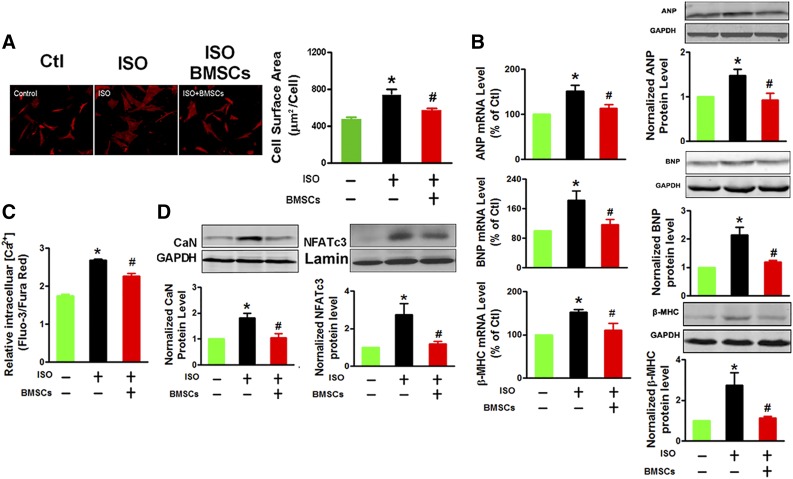
Figure 1.
BMSCs inhibit ISO-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. (A): BMSC coculturing suppresses the hypertrophic growth of neonatal rat ventricular cells (NRVCs) induced by β-adrenoceptor agonist ISO, as indicated by reduced cell surface area. The images represent immunostaining with α-actinin antibody (red signal; magnification ×200, at least 10 randomly selected fields in three separate experiments), and the bar charts are averaged cell surface area. (B): BMSC coculturing suppresses ISO-induced expression of the hypertrophic marker genes ANP, BNP, and β-MHC at both mRNA and protein levels in NRVCs, measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immunoblotting analyses, respectively. (C): BMSC coculturing suppresses ISO-induced Ca2+ overload as indicated by the lowering of intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in NRVCs. (D): BMSC coculturing suppresses ISO-induced upregulation of CaN (left) and NFATc3 (right) proteins in the nuclei of NRVCs. The data were obtained from three independent experiments. ∗, p < .05 versus Ctl; #, p < .05 versus ISO. Abbreviations: BMSC, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell; CaN, calcineurin; Ctl, control; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ISO, isoproterenol; β-MHC, β-myosin heavy chain; NFATc3, nuclear factor of activated T cells cytoplasmic 3.