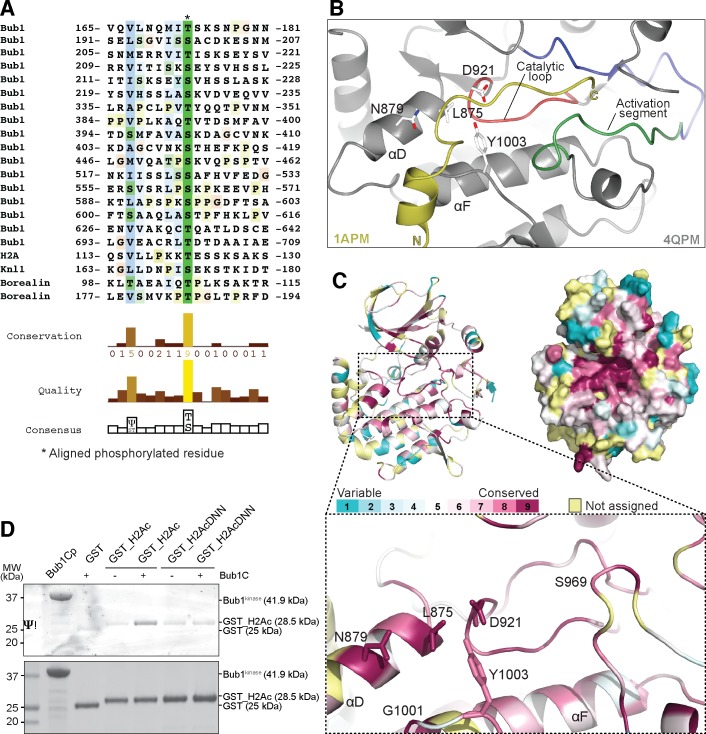
Fig 4. Bub1kinase possesses conserved residues that recognize a substrate consensus sequence.
(A) Alignment of phosphorylation sites found in Bub1-dependent phosphorylation reactions using the ClustalX algorithm in Jalview [54]. Numbers indicate boundaries of the protein segments shown; phosphorylated residues are denoted with an asterisk, the conservation of residues is highlighted using the ClustalX coloring scheme. (B) The structure of Bub1kinase (PDB ID 4QPM) was superimposed onto the structure of PKA bound to a pseudo-substrate inhibitor [PDB ID 1APM, reference [55]]. The image shows only Bub1 and the position of the pseudo-substrate peptide (yellow) after alignment of PKA to Bub1. Bub1 residues putatively involved in substrate recognition are depicted as sticks. (C) Bub1kinase sequence and structure conservation. The same residues as in (B) are shown in sticks. Conservation was determined by aligning Bub1kinase from 14 organisms with ConSurf [56], the scoring legend is depicted on the upper left. Conservation scores obtained for positions in the alignment that had less than 6 un-gapped amino acids were considered to be unreliable and colored light yellow in the graphic visualization output. Images were created with CCP4MG [53] and Pymol (Schrödinger LLC, Portland, OR). (D) Bub1kinase-dependent H2A phosphorylation can be reduced by mutating V115D, L116N, L117N on H2A. GST-H2A constructs were incubated with Bub1kinase and ATP, then analyzed by SDS PAGE, and phosphorylated proteins were specifically stained using Pro-Q® Diamond Phosphoprotein Gel Stain.