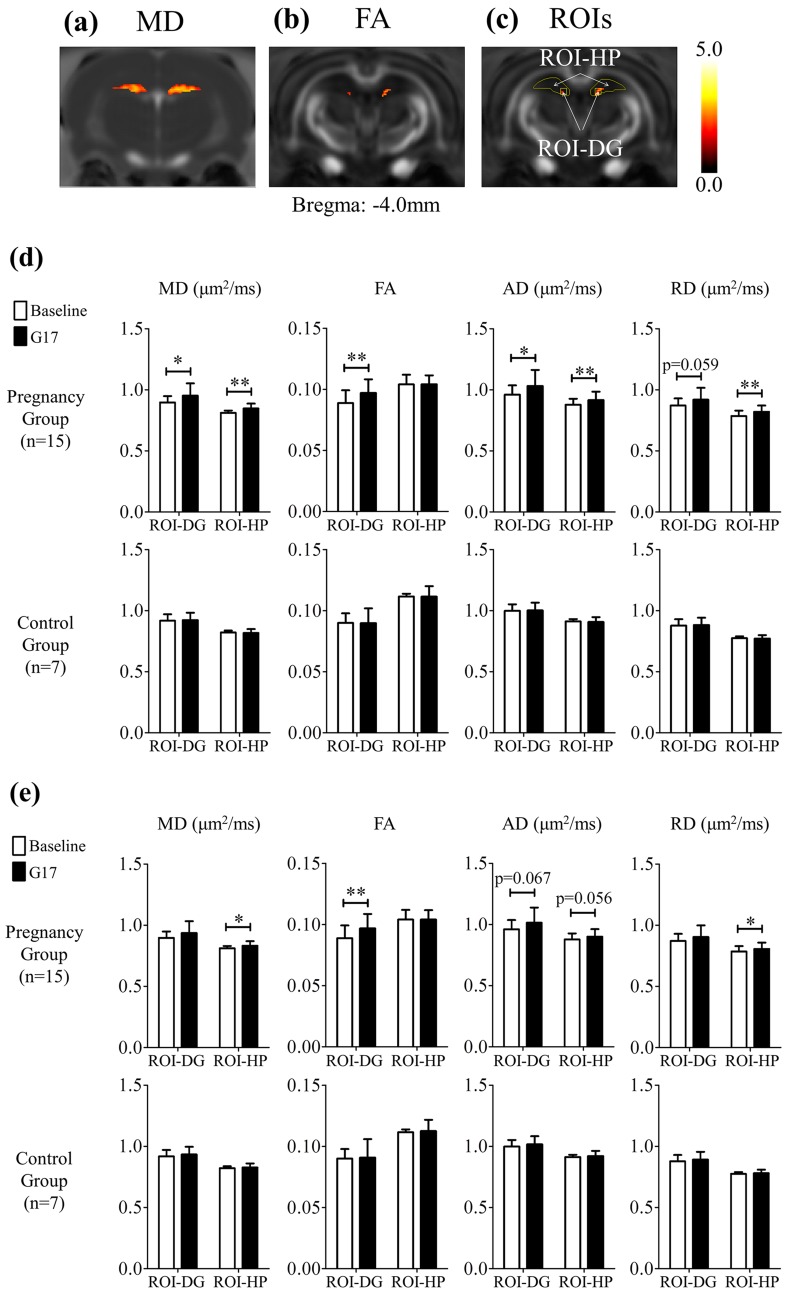
Fig 3. The results of the voxel-based analysis followed by multiple testing corrections via false discovery rate in MD (a) and FA (b) of the pregnancy group. The hot voxels indicated significant increase during pregnancy, and the threshold applied was p = 0.05. With reference to (a), (b) and the rat brain atlas, regions of interest (ROIs) were defined (c) and employed for quantitative analysis. The ROI-HP covers the dorsal hippocampus, and the ROI-DG covers the dorsal dentate gyrus (DG). (d) The summary of the local tissue structural changes between the baseline and G17 in the ROI-DG and ROI-HP of both the pregnancy and control groups without any normalization. There was significant increase in FA in the ROI-DG, and significant increase in MD, AD and RD in the ROI-HP during pregnancy, but not in the controls. After normalization with global GM changes (e), MD, AD and RD changes in ROI-HP became smaller but remained increased, while the increase in FA in the ROI-DG was similar. These results indicated the presence of more pronounced tissue structural remodeling in the dorsal hippocampus, including the dorsal dentate gyrus during pregnancy. Two-way ANOVA was applied, followed by post-hoc Bonferroni’s test.
* and ** denote p<0.05 and p<0.01 and, respectively. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.