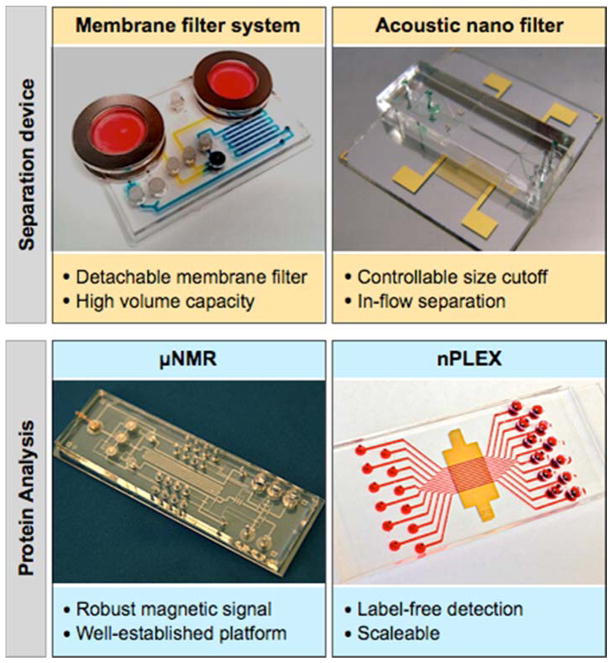
Figure 3. Miniaturized devices developed for exosome separation (top) and its protein profiling (bottom).
Images are adapted with permission from: Shao H, Chung J, Balaj L et al. Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nat Med 2012;18:1835–1840 [17]; Im H, Shao H, Park YI et al. Label-free detection and molecular profiling of exosomes with a nano-plasmonic sensor. Nat Biotechnol 2014;32:490–495 with permission from Nature Publishing Group, copyright 2014 [18]; with permission from Rho J, Chung J, Im H et al. Magnetic Nanosensor for Detection and Profiling of Erythrocyte-Derived Microvesicles. ACS Nano 2013;7:11227–11233. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society [31]; and with permission from Lee K, Shao H, Weissleder R, Lee H. Acoustic purification of extracellular microvesicles. ACS Nano 2015;9:2321–2327. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society [32].