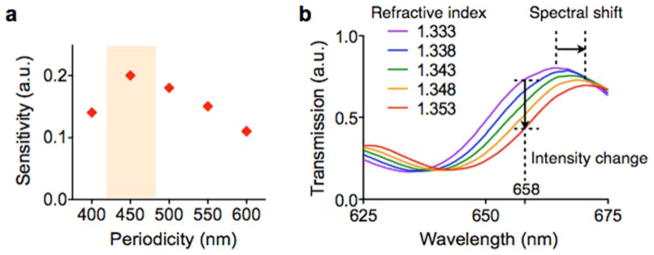
Fig. 5. Device design optimization.
(a) The sensitivity of the nPLEX sensor was defined as Δλ/w, where Δλ and w are the shift and the width of SPR spectrum, respectively. The nanohole array with 450-nm hole-pitch showed the highest sensitivity for the detection of 100 nm exosomes. a.u., arbitrary unit. (b) Increase in the refractive index on the nPLEX surface induces a spectral shift (Δλ) of resonance peak to a longer wavelength. The increase of refractive index also causes intensity changes (Δp) at a given wavelength (e.g., at 658 nm). Therefore, exosome binding can be detected by either tracking Δλ by spectrometry or Δp by imaging. Reproduced from Im H, Shao H, Park YI et al. Label-free detection and molecular profiling of exosomes with a nano-plasmonic sensor. Nat Biotechnol 2014;32:490–495 with permission from Nature Publishing Group, copyright 2014 [18].