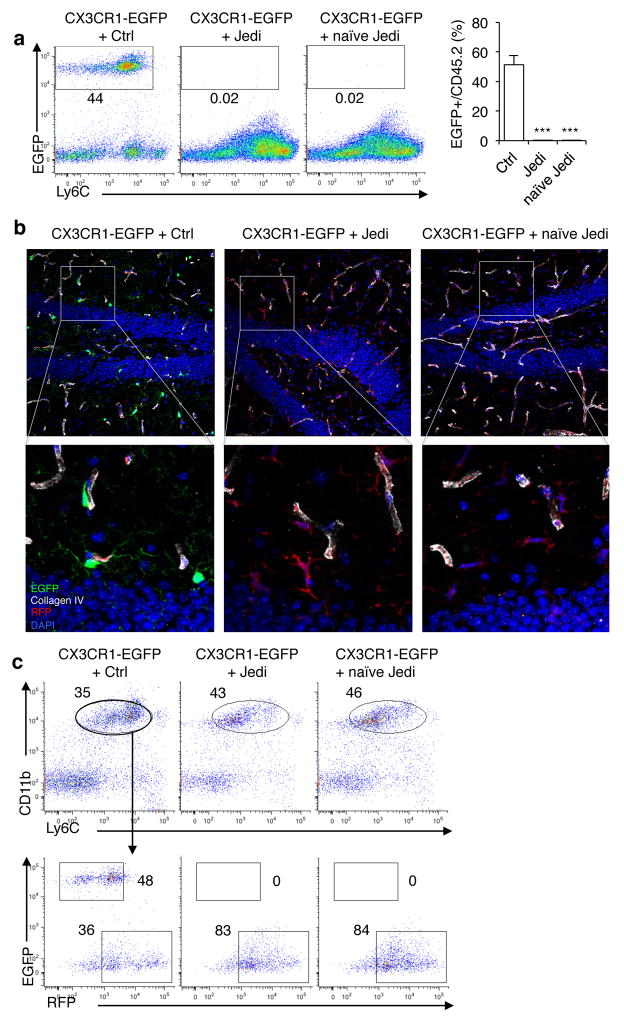
Figure 2. JEDI T-cells reveal naïve T-cell can cross the blood brain barrier and kill antigen-expressing microglia.
(a) CX3CR1-EGFP mice were transplanted with bone marrow from actin-Red Fluorescence Protein (RFP) mice. Ten weeks later mice were injected with 5×105 Ctrl or JEDI CD8+ T-cells. A cohort were vaccinated with EGFP while another cohort was not vaccinated (naïve JEDI). Quantification of EGFP-expressing microglia was performed 1 week after T-cell transfer. Representative plots are shown (left). Graph (right) presents the mean±s.d. of the frequency of microglia in the brains of the mice (n=3 mice/group). ***P<0.001 vs Control-treated. (b) Representative images of the dentate gyrus of hippocampus 3 weeks after injection of the CD8+ T-cells and 13 weeks after BMT. Collagen IV denotes vessel basement membrane. 20x magnification, bar represents 50 μm. (c) The brains of CX3CR1-EGFP mice transplanted with RFP-expressing BM, and injected with Ctrl or JEDI CD8+ T-cells at 10 weeks post-BMT (as in c), were analyzed 3 weeks after injection of the T-cells to quantitate the number of EGFP+ and RFP+ microglia (CD45intLy6cintCD11b+). Representative flow cytometry plots are shown from n=3 mice/group.