Figure 3.
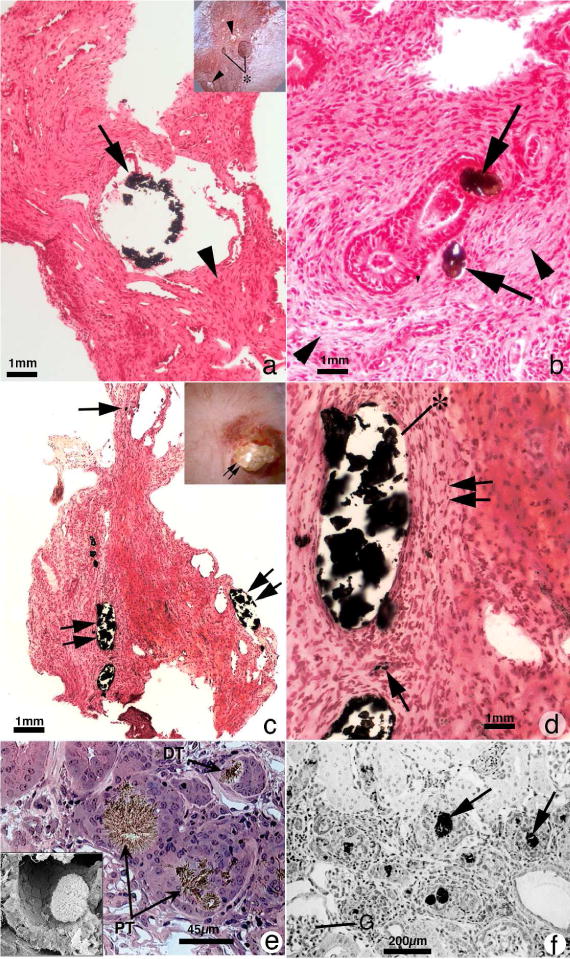
Histopathology of renal papilla from primary hyperoxaluria, cystine and DHA stone formers. Panel A is a histologic section from a primary hyperoxaluric stone former with normal renal function showing isolated dilated IMCD filled with CaOx mineral (arrow) encased in regions of extensive interstitial fibrosis (arrowhead). Sites of interstitial plaque were rare. Insert to panel A shows endoscopic view of papillum from a primary hyperoxaluric stone former characterized by a few dilated ducts of Bellini with and without (asterisk) protruding plugs were seen scattered between sites of yellow plaque (arrowheads). Panel B is a higher magnification Yasue-stained tissue section showing regions of extensive interstitial fibrosis adjacent to and away from (arrowheads) sites of intraluminal IMCD deposits. Panel C is a Yasue-stained histologic section from a patient with cystine stones revealing numerous dilated IMCD (double arrows) and BD plugged primarily apatite with a few BD containing cystine deposits. Occasionally a thin loop of Henle was noted plugged with apatite deposits (arrow). Panel D is a higher magnification image of a region from panel C showing extensive interstitial fibrosis (double arrow) adjacent to sites of intraluminal IMCD deposits (asterisk) and an occasional site of interstitial plaque (arrow). Panels E and F show the morphology of 2,8-dihydroxyadenine (DHA) crystal in kidneys from adenine phosphoribosyltranserase (Aprt)-deficient mice that resembles human Aprt deficiency. In panel E two proximal (PT, arrows) and a distal tubule (DT, arrow) is seen, each with large brownish-red crystals in the tubular lumens. Interstitial fibrosis is noted around glomeruli and various tubular segments. The insert in panel E shows by scanning electron microscopy an individual DHA crystal in the lumen of a proximal tubule. Panel F shows numerous DHA crystals (arrows) in the cortex of an Aprt-deficient mouse with advanced pathology (score of 4) characterized by interstitial fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis (G).
