Figure 1. Simplified map depicting inhibitory transmission in the hypoglossal motor nucleus (XIIn, left side of figure) and preBötzinger complex (preBötC, right side).
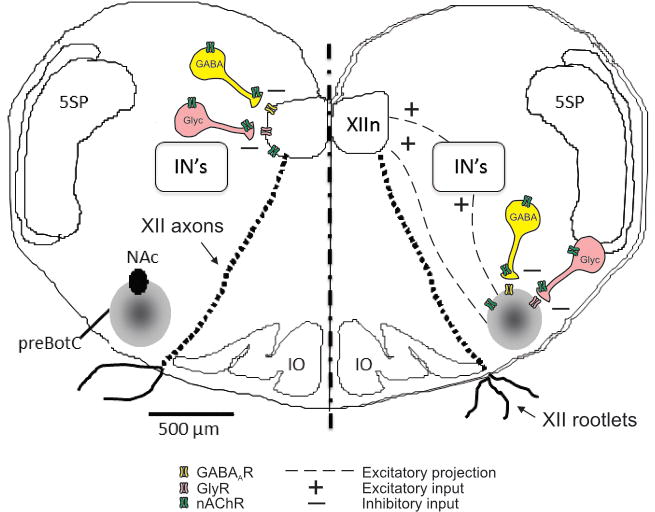
As shown, excitatory synaptic input from the preBötC to the XIIn is transmitted both directly and via interneurons (IN’s) (Koizumi et al., 2008). Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are found postsynaptically on both preBötC and hypoglossal motoneurons, and also on the soma and terminals of GABAergic and glycinergic interneurons. As described in text, activation of presynaptic nAChRs increases the release of GABA and glycine. Both preBötC interneurons and XII motoneurons also express GABAA receptors (GABAAR) and glycine receptors (GlyR). Chronic nicotine exposure desensitizes nAChRs, which can modify both presynaptic release of GABA and glycine, and the expression of postsynaptic GABA and glycine receptors. In our experiments, we are assuming that acute injection of muscimol or glycine into XIIn or preBötC activates primarily postsynaptic GABA and glycine receptors on preBötC interneurons and XII motoneurons (but refer to text for a description of possible presynaptic influences as well). NAc, compact formation of nucleus ambiguous; 5SP, spinal trigeminal nucleus; IO, inferior olivary nucleus. XII motor axon tracts and XII rootlets emerging from the ventral surface are also shown; as described in methods, we recorded XII motoneuron population activity from the rootlets. PreBötC population activity was recorded with a suction electrode placed over the preBötC.
