Figure 8.
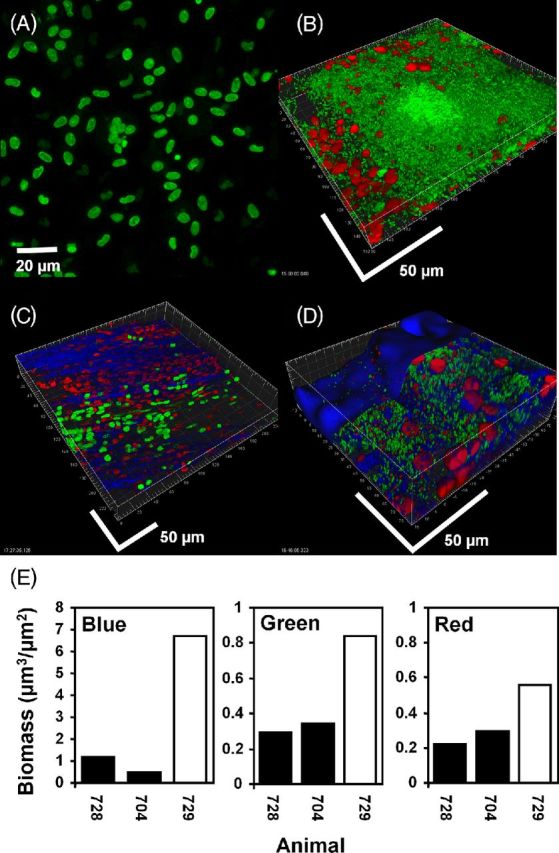
Mucosal P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm in the bulla in the chinchilla stained for cells with live (green) / dead (red) kit and KMnO4 (blue). (A) and (C): uninoculated controls. The nuclei of host epithelial cells stained initially primarily with Syto 9 (green) but over the imaging time became red as they absorbed PI. Cells with approximate equal proportions of the two stains appeared yellow. KMnO4 revealed matrix material between the cells. (B) and (D): bullae from two animals inoculated with PAO1. Bacterial rods stained green indicating that they were viable. Unlike the host cells, bacterial cells did not integrate PI, making the majority of bacteria readily distinguishable from the nuclei of host cells on the basis of size, morphology and differential staining. (D) After staining with KMnO4 material between and colocalized with the biofilm cell clusters was visible (blue). Biofilm bacteria and the nuclei of host cells did not appear morphologically or structurally different from the specimen stained only with the BacLight kit. Scale bars = 50 μm. (E) COMSTAT analysis of confocal images from the bullae of two uninoculated animals (black bars) and an animal infected with PAO1 (open bar) stained with BacLight LIVE/DEAD kit and KMnO4 and RM. Reflected signal from the KMnO4 (blue), live bacteria (green) and host nuclei (red).
