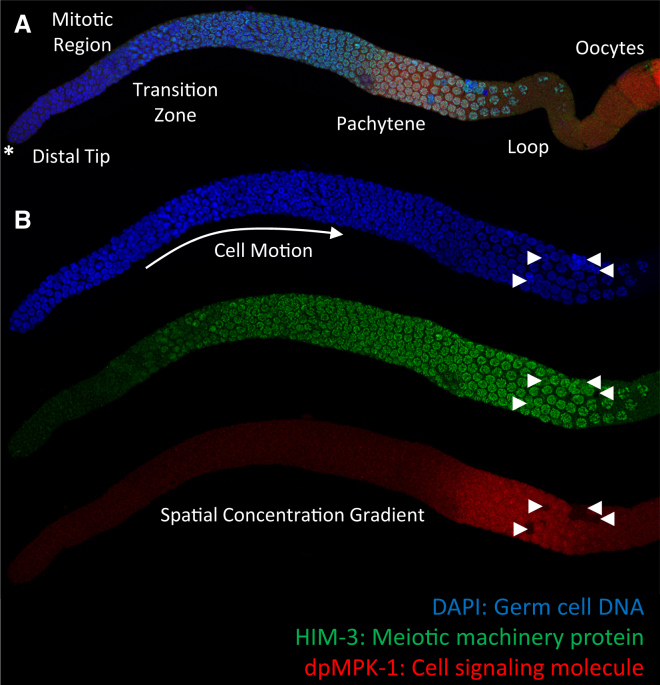
Figure 1.
An adult, hermaphrodite C. elegans germline. (A) Shows the anterior region of the germline, from the distal tip (left in the image, marked by an asterisk) through the first few cellularized oocytes (right in the image). (B) Focuses on the germline from (A), but zoomed in only on the region from the distal tip to the loop. (Blue) Nuclei stained with DAPI. Mitotic cells in the mitotic region undergo divisions that maintain the germ cell population. As the cells divide and expand the mitotic region, more mature cells are pushed toward the loop. (Green) Germ cells differentiate in the transition zone, entering meiosis, marked by the HIM-3 protein. HIM-3 labels the synaptonemal complex axis of the meiotic nuclei (53). (Red) Activation of MPK-1, which occurs in the final two-thirds of the anterior germline. Near the loop, a large fraction of arriving germ cells undergo apoptosis (apoptotic cells in each color channel marked by white arrowheads). Surviving cells pass the loop and become oocytes. To see this figure in color, go online.