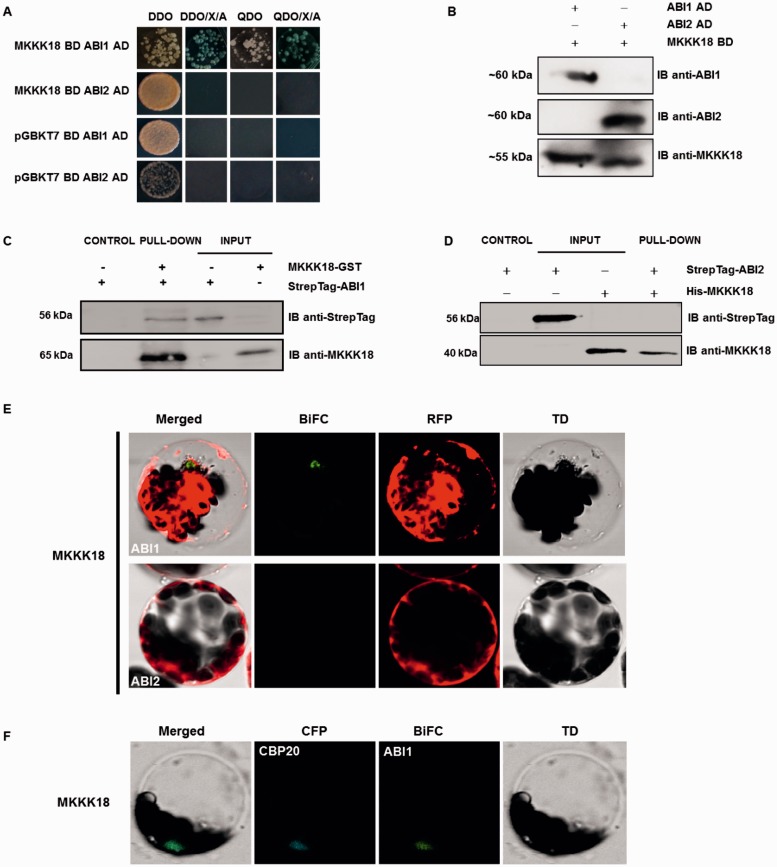
Fig. 6.
MKKK18 interacts with the ABI1 protein phosphatase. (A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of the interaction between MKKK18 and ABI1/2 PP2Cs. Diploid yeast colonies were grown on double (DDO-SD medium without Leu and Trp) or quadruple selective medium (QDO-SD medium without Leu, Trp, His or Ade) with or without supplemented X-α-Gal and aureobasidin. The bait (MKKK18) did not autoactivate the reporter genes in yeast. (B) Detection of ABI1/2 and MKKK18 expression in diploid yeast strains. Expression of BD and AD fusion proteins in yeast was determined by immunoblotting using specific anti-ABI1, anti-ABI2 and anti-MKKK18 antibodies. (C and D) Pull-down assays to verify the interaction of ABI1/2 with MKKK18. Input lines represent 100% of the ABI1/2. Recombinant GST–MKKK18 or His-MKKK18 was pre-coupled to glutathione–Sepharose, and incubated with StrepTag-ABI1 or StrepTag-ABI2, respectively. Pulled-down StrepTagged ABI1 protein was detected (IB) with the epitope tag antibody. The presence of recombinant protein was confirmed using anti-MKKK18 antibody. (E and F) ABI1–MKKK18 interaction occurs within the nucleus. BiFC analysis in Arabidopsis protoplasts expressing full-length ABI1/2 and MKKK18 fused to cECFP or nVenus, respectively. RFP (E) was used as a transformation control. CFP–CBP20 (cyan fluorescent protein–Cap Binding Protein 20) (F) was used as a marker of nuclear localization.