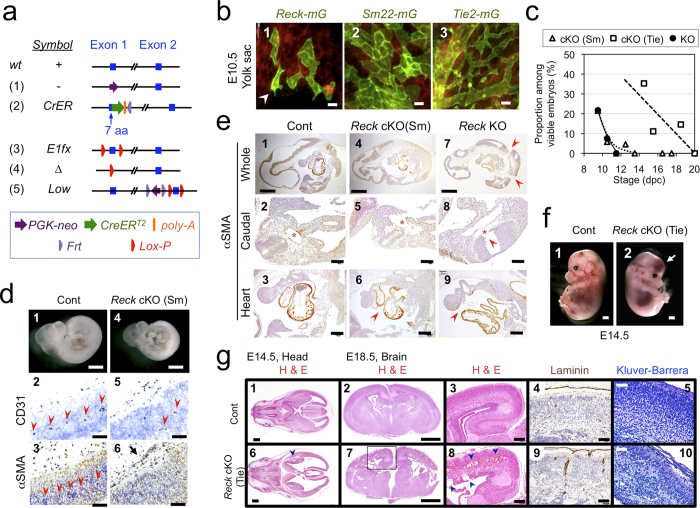
Figure 1. Cell type-selective inactivation of Reck in vivo using Sm22-Cre or Tie2-Cre mice.
(a) Reck alleles used in this study. (b) Cells that expressed Reck (1), Sm22 (2, mural cells), or Tie2 (3, endothelial cells) emitted green fluorescence in the yolk sac of E10.5 embryos. For Reck, a pregnant mouse was injected with tamoxifen at 8.5 dpc. Arrowhead indicates a cell with ambiguous morphology. (c) Viability of global Reck KO mice (Reck−/−, filled circles with solid line) or tissue-selective Reck knockouts, Reck cKO (Sm) [ReckE1fx/∆; Sm22-Cre, triangles] or Reck cKO (Tie) [ReckE1fx/∆; Tie2-Cre, square]. Expected frequency was 25% in all cases. (d) Morphology of control (ReckE1fx/∆) and Reck cKO (Sm) mice at E10.5. Whole embryo (panels 1, 4) and the dorsal, peri-neural area of serial sagittal sections, immunostained for CD31 (panels 2, 5) or αSMA (panels 3, 6), are shown. Brown signals indicate immunoreactivity. Arrow indicates an abnormal peri-neural vessel. Arrowheads highlight CD31-positive small vessels within the neural tube. (e) Distribution of αSMA-immunoreactivity in the sagittal sections of control, Reck cKO (Sm), and Reck KO mice at E10.5. Whole section (top row), caudal area containing a cross-sectional view of the neural tube and dorsal aorta (second row), and the heart (third row) are shown. Arrowheads show broken sites in panels 7, 8 and missing pericardial membrane in panels 6, 9. Asterisks highlight dorsal aorta. (f) Gross morphology of the control (ReckE1fx/∆) and Reck cKO (Tie) mice at E14.5. Arrow indicates intra-cranial hemorrhage. (g) Brain morphology in sections of control (upper panels) or Reck cKO (Tie) mice (lower panels) at E14.5 (panels 1, 2, 6, 7) or E18.5 (3–5, 8–10) that were subjected to hematoxylin and eosin (panels 1–3, 6–8), anti-laminin (panels 4, 9), or Kluver-Barrera (panels 5, 10) staining. Arrowheads indicate intra-cranial hemorrhage. Scale bar: (b) 20 μm; (d) 1 mm (1, 4), 50 μm (other panels); (e) 1 mm (1, 4, 7), 100 μm (2, 5, 8), 200 μm (3, 6, 9); (f) 1 mm; (g) 1 mm (1, 2, 6, 7), 200 μm (3, 8), 100 μm (4, 9), 50 μm (5, 10).