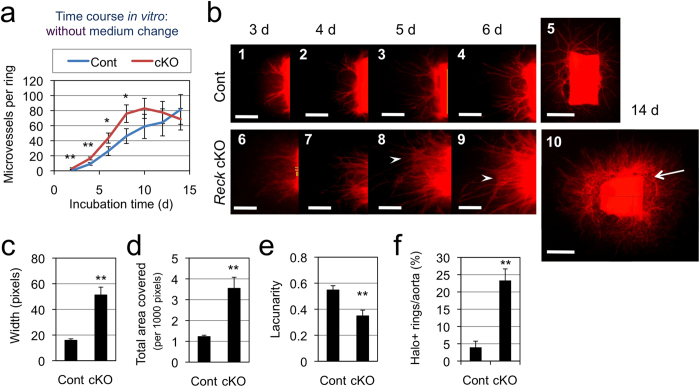
Figure 2. Effects of Reck-deficiency on microvessel formation in ARA.
(a) Time course of microvessel formation (number per ring). Aortic rings from 5-weeks old control (Reck+/CrER; mTmG, blue line, n = 9) or Reck cKO (ReckE1fx/CrER; mTmG, red line, n = 4) mice were subjected to ARA (no medium change), and the number of microvessels was counted every other day from day 2 to 14. (b) Fluorescent micrographs of a control (panels 1–5) or Reck cKO (panels 6–10) ring after incubation for indicated period of time in ARA without medium changes. Arrow indicates peri-aortic halo, and arrowheads highlight aggregating microvessels. Scale bar: 1 mm (5, 10), 0.5 mm (other panels). (c) Relative width of microvessels measured using ImageJ on high magnification images. Summary of 6 independent experiments (n = 36 rings for Cont and 30 rings for Reck cKO in total). (d, e) Parameters measured using AngioTool44. Summary of 8 independent experiments for Cont (46 rings) and 7 experiments for Reck cKO (43 rings). (f) Frequency of rings exhibiting peri-aortic halo. Summary of 6 independent experiments for Cont (78 rings) and 3 independent experiments for Reck cKO (30 rings).