Fig. 6.
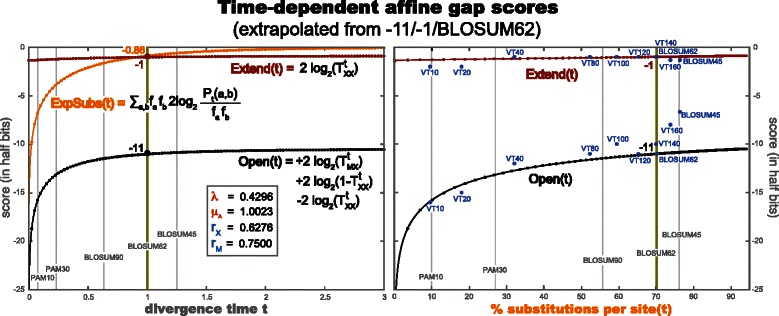
Explicit continuous-time affine-gap cost functions (based on the AFR evolutionary model) extrapolated from the commonly used -11/-1 gap cost of standard sequence/sequence Smith-Waterman comparisons. Time-dependent synchronized parameterization of the substitution score with its corresponding gap open and gap extend costs based on the AFR evolutionary model. The parameterization is such that for time t=1, it corresponds to a gap open cost of -11, a gap extend of -1, and the BLOSUM62 scoring matrix. In the left figure, the gap-open and gap-extend functions and the expected substitution score are depicted as a function of the divergence time. In the right figure, the gap-open and gap-extend functions are depicted as a function of the fraction of substitutions at that time, defined as . The blue dots correspond to gap-open and gap-extend values empirically determined for SSEARCH with different substitution matrices in [28]. (The gap scores for the VT160 and BLOSUM50 matrices originally given in 1/3 bits have been rescaled to half bits)
