Fig. 7.
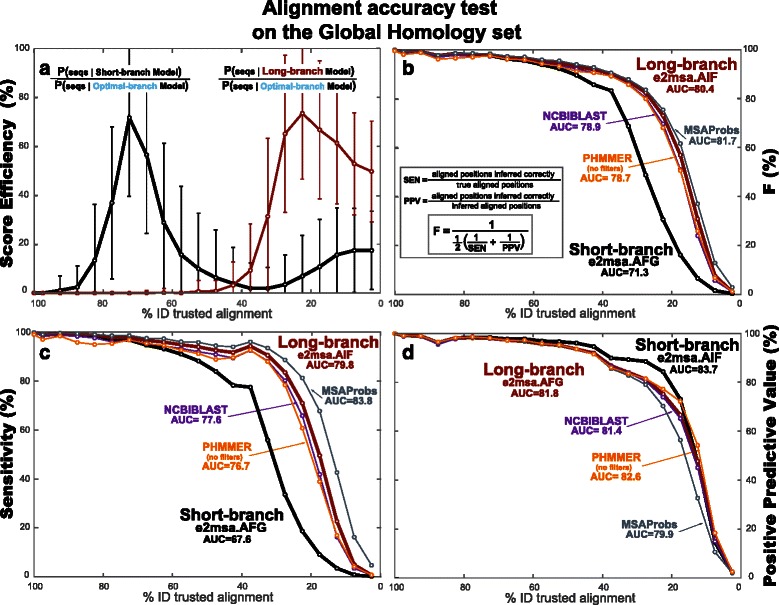
The score efficiencies for a long-branch versus a short-branch parameterized model have no correspondence with alignment accuracy for the Global Homology set. a For the long-branch and short-branch parameterizations of the AIF model in e2msa, we present their score efficiency as a function of the percentage identity of the alignments. Alignments are binned in 5 % identity groups (relative to the trusted alignments). For each identity bin, the mean and standard deviation of the score efficiency are calculated. b For the long-branch and short-branch models, we present the accuracy of the alignments inferred by e2msa. Alignment accuracy is calculated using the F measure that combines sensitivity (the fraction of aligned positions inferred correctly) and positive predictive value (the fraction of inferred aligned positions that are correct). We present comparisons with the methods NCBIBLAST, PHMMER, and MSAProbs. Panels (c) and (d) report the sensitivity (SEN) and positive predictive value (PPV) measures respectively for completeness
