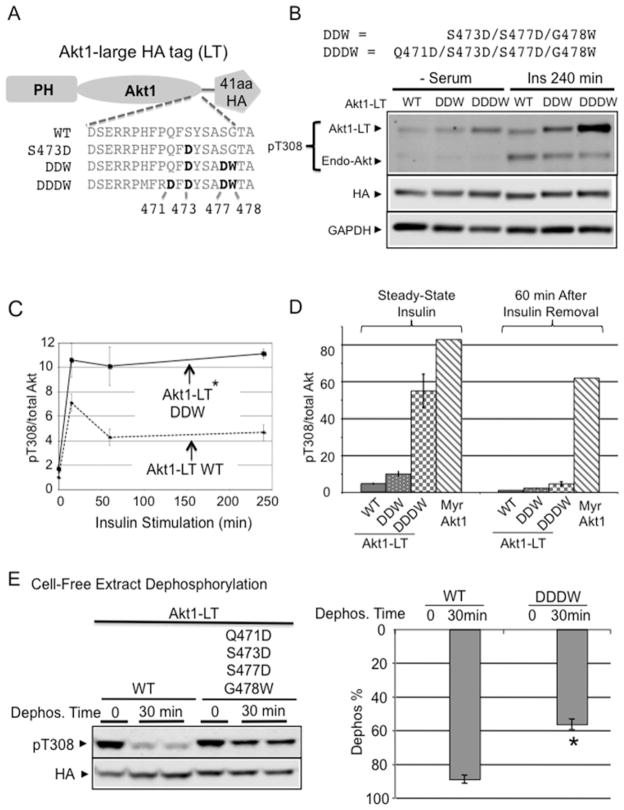
Figure 5. C-terminal stabilization in full-length Akt enhances insulin responsiveness.
(A) To differentiate from endogenous Akt, a 41-amino-acid LT containing the HA epitope was fused with Akt1 (Akt1-LT). C-terminal mutation constructs in Akt1-LT are shown. (B) Akt1-LT-DDW and Akt1-LT-DDDW progressively improved insulin sensitivity after chronic insulin stimulation (240 min). Indicated Akt1-LT constructs were transfected into H9C2 myoblasts and stimulated with 2 μM insulin for 240 min. Protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies to phospho-Akt Thr308 and anti-HA. (C) The graph shows the time course of phospho-Thr308 response after insulin stimulation. Quantification shows the pThr308/total Akt ratio after 4 h of insulin stimulation normalized to Akt1-LT WT. *P < 0.05 Akt1-LT DDW (n=3) compared with Akt1-LT WT (n=4). (D) Unlike phospho-Myr-Akt1, pThr308 in Akt1-LT-DDDW was rapidly dephosphorylated after insulin removal. H9C2 cells were pre-stimulated with insulin for 10 min and then insulin medium was replaced with serum-free medium and incubated for 60 min. Quantification shows pThr308/total Akt ratio after 60 min of insulin removal. (E) DDDW modification provided Thr308 dephosphorylation resistance similar to full-length PIFtide in cell-free extracts. After maximally phosphorylating both AKT1-LT-WT and AKT1-LT-DDDW by insulin/pervanadate/PDK1 treatment, flash-frozen cell extracts were incubated at 30°C for 30 min. After incubation, protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies detecting phosphorylated Akt (Thr308) and HA epitope. The histogram shows the percentage of Akt dephosphorylation at 0 min and at 30 min (Dephos. %) (respectively, Akt1-LT WT, n=5, n=10; Akt1-LT-DDDW, n=2, n=5). *P < 0.001 compared with Akt1-LT-WT at 30 min. See also Supplementary Figure S4 for Akt1-LT-PIF compared with Akt1-LT-DDDW assay.