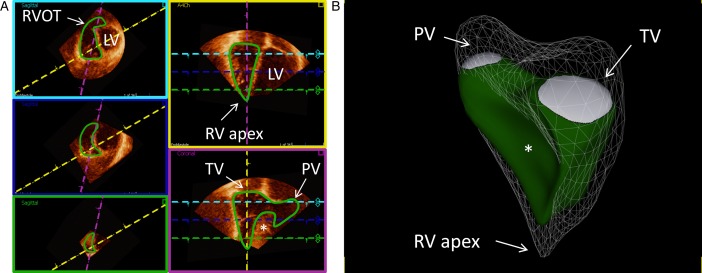
Figure 4.
Example of delineation of a normal right ventricle (RV) in end-diastole showing the endocardial contour detection in green. (A) The three left images (magenta, blue, and green boxes) are the short-axis views at different levels with the left ventricle (LV) to the right of the interventricular septum (*). The upper left image (magenta box) is closer to the base and right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) and the lower image (green box) closer to the apex. The upper right image (yellow box) is a four-chamber view and the lower right image (purple box) is a right ventricular three-chamber view with tricuspid valve (TV), apex, and pulmonary valve (PV) in the same projection. The dashed colored lines represent the plane of the boxes with the corresponding color. (B) Example of a three-dimensional echocardiographic reconstruction of the delineation of the right ventricle seen from the septal side (end-diastolic volume 153 ml, end-systolic volume 64 ml, and ejection fraction 58%). The mesh is the right ventricle at end-diastole, in green at end-systole. Pulmonary valve (PV) is shown in white in the upper left side, tricuspid valve (TV) is shown in the upper right side, and right ventricular (RV) apex toward the bottom. *shows the interventricular septum bulging into RV. Data were processed using a dedicated software (4D RV-Function, TomTec Imaging Systems). See also Video 1.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a