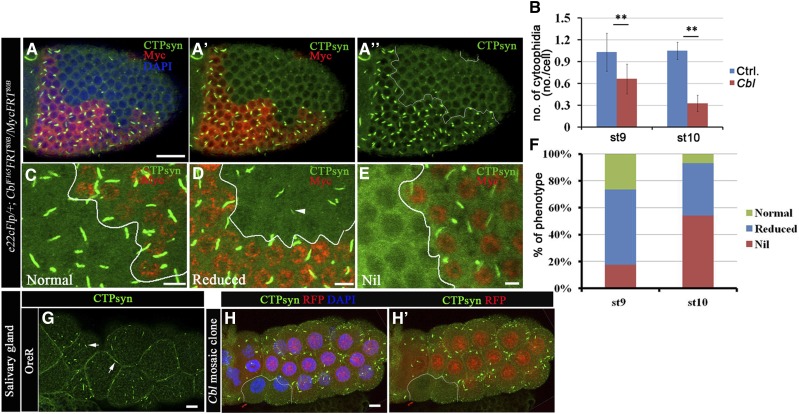
Figure 2.
Cbl regulates the CTPsyn filamentous structure. (A–F) Merged confocal sections of stage 9–10 egg chambers stained with anti-CTPsyn (green) and anti-Myc (red) antibodies (A–A′′). Myc-positive signals marked wild-type and Cbl heterozygous cells, whereas Cbl homozygous mutant cells were marked by the absence of Myc staining. (B) Average numbers of CTPsyn filaments/cell were calculated from stage 9 and 10 egg chambers of the genotype e22cFlp/+; Cbl F165FRT80B/MycFRT80B. (C) Normal CTPsyn filament structures are shown in green and are represented by the green columns in F. The “reduced” phenotype (F, blue column) indicates a shortening (arrowhead in D) of CTPsyn filaments in Cbl mutant cells. The nil phenotype (red column) represents the lack of CTPsyn filaments (34 and 72 egg chambers at stages 9 and 10, respectively). (G) Larval salivary glands of OreR were stained with anti-CTPsyn antibody. CTPsyn filamentous structures are shown in green (arrow). (H–H′) Larval salivary glands containing a clone of Cbl mutant cells are marked by the absence of RFP (outlined in white) and stained with anti-CTPsyn (green) antibody. The results are shown as the mean ± SD; **P < 0.01. Bar, 20 μm.