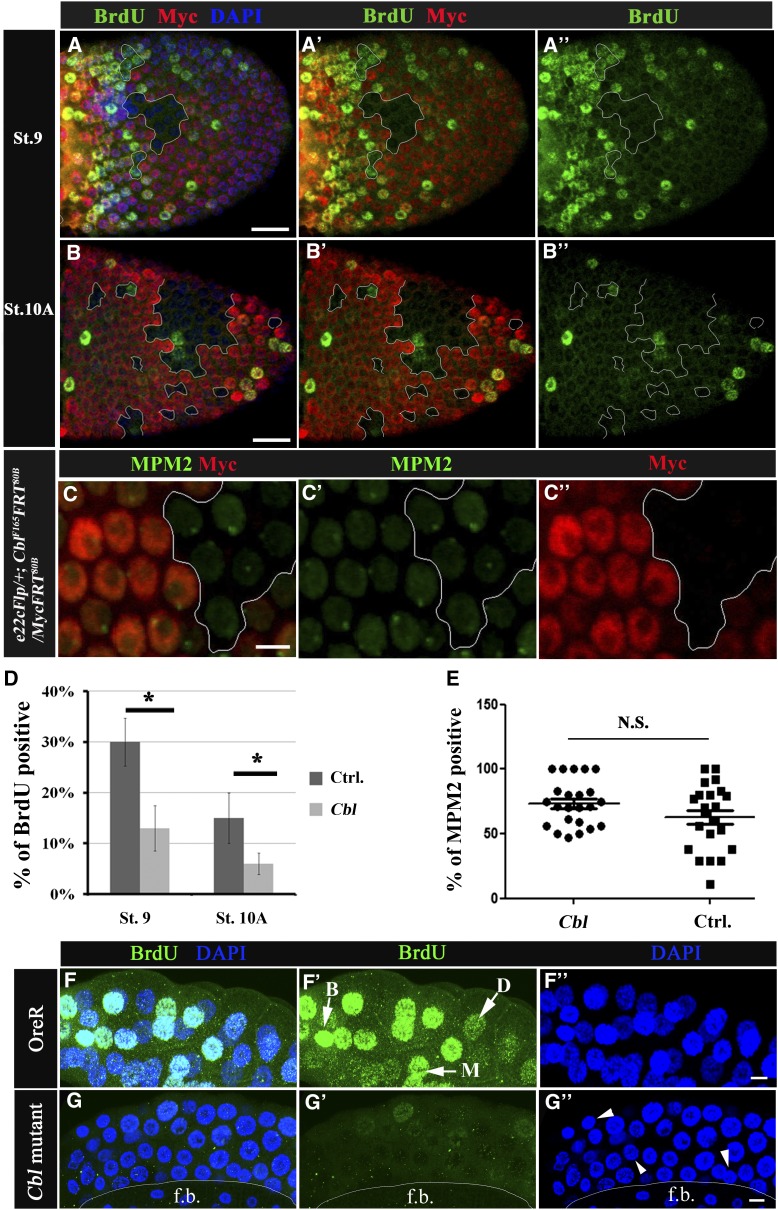
Figure 4.
Cbl is involved in the endocycle. (A–C′′) Mosaic egg chambers containing Cbl mutant follicle cell clones. Cells are labeled as described in Figure 2. (A–B′′) BrdU incorporation is shown in the follicular epithelium containing mosaic clones for Cbl (Myc-negative cells, outlined in white) of stage 9 (A–A′′) and stage 10A (B–B′′) egg chambers. The BrdU signal is in green; nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (C–C′′) The MPM2 signal (in green) was detected in Cbl mutant cells and wild-type follicle cells in stage-9 egg chambers. (D) Percentages of BrdU-positive vs. Myc-negative cells (Cbl, light gray column) and Myc-positive twin clone cells with wild-type Cbl genes (Ctrl, dark gray column). Results are shown as the mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05. There were 16 and 18 egg chambers at stages 9 and 10, respectively. N = 3. (E) MPM2 positivity was assessed as described above; N.S. indicates not significant. (F–G′′) BrdU incorporation (shown in green) in wild-type (F–F′′) and in Cbl homozygous (G–G′′) salivary glands. In F′, BrdU signals were classified as bright (B), medium (M), or dark (D) (arrow). (F′′ and G′′) DNA was stained with DAPI (blue), and a reduction in nuclear size in Cbl mutant (arrowhead in G′′) was observed. f.b. indicates fat bodies. Bar, 20 μm.