Figure 5.
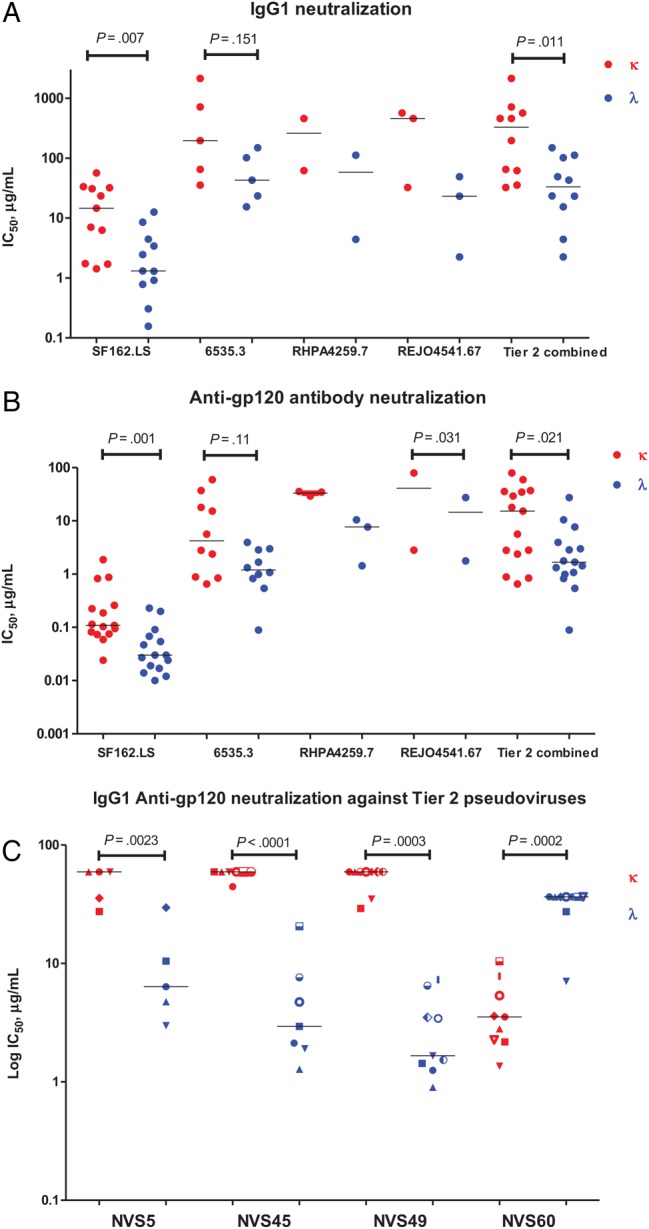
Neutralization of light chain fractionated samples against clade B tier 1 and tier 2 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) pseudoviruses. Paired patient immunoglobulin G (IgG) samples were tested for neutralizing activity against the indicated pseudoviruses as described in “Materials and Methods” section. Assays were run in duplicate. The x-axis demonstrates pseudovirus or patient tested. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) titer was calculated as the immunoglobulin concentration that caused a 50% reduction in relative luminescence units (RLU), compared with the virus control wells, after subtraction of cell control RLU (left y-axis). For panels A and B, each circle represents individual patient fractions (red represents κ fractions, and blue represents λ fractions), and for panel C, symbols represent individual pseudoviruses (red represents κ fractions, and blue represents λ fractions). Combined tier 2 refers to IC50 values against 6535.3, RHPA4259.7, and REJO4541. Sixty-seven pseudoviruses were plotted together. A, IgG1 κ and λ fraction testing (n = 15) reveals more potency for neutralization (ie, a lower IC50) in λ fractions. B, Anti-gp120 κ and λ fraction testing (n = 15) reveals more potency for neutralization in λ fractions. C, Anti-gp120 IgG1 κ and λ fractions from 4 patients with known broad neutralizing activity (NVS5, NVS45, NVS49, and NVS60) were tested at equal starting concentrations against an individualized panel of known tier 2 pseudoviruses their plasma has activity against. Three of 4 patients demonstrated more-potent neutralization in the λ fraction.
