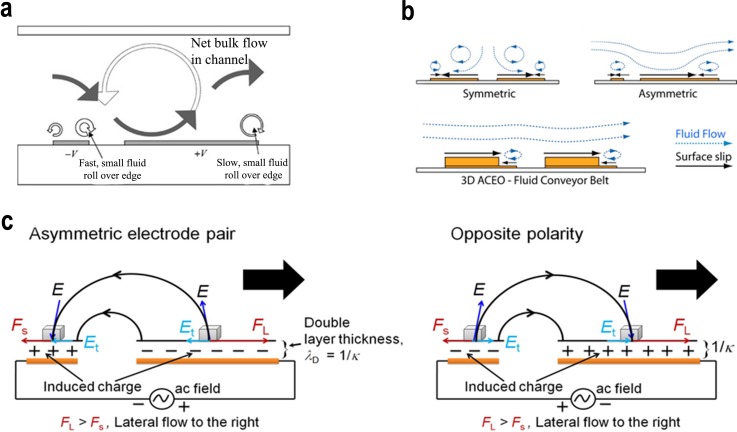
FIG. 3.
Schematic representation of (a) physical mechanism of ac electro-osmosis in an asymmetric electrode array inside a microfluidic channel. Reprinted with permission from Ramos et al., Phys. Rev. E 67, 056302 (2003). Copyright 2003 American Physical Society. (b) Fluid flow generated by an AC field applied across two planar symmetric, asymmetric, and partially raised electrodes. Reprinted with permission from Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(14), 143508 (2006). Copyright 2006 AIP Publishing LLC. (c) Mechanism of AC-EHD induced fluid flow using asymmetric electrode pair. Reversing the polarity of the AC field also reverses the sign of the charges in the induced double layer, and since electrical body forces are the product of the charges and the applied field, a steady flow can be maintained towards the large electrode. Reprinted with permission from Shiddiky et al., Sci. Rep. 4, 3716 (2014). Copyright 2014 Nature Publishing Group.