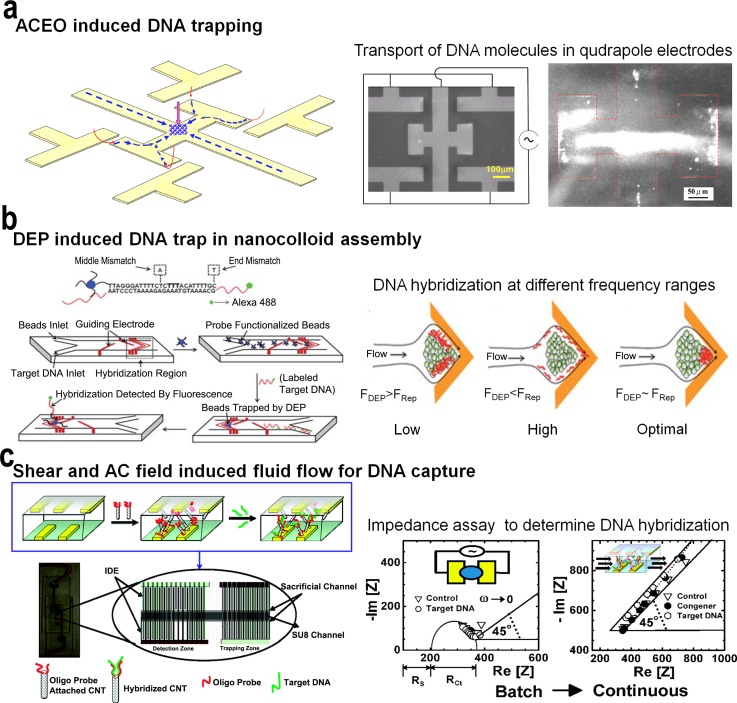
FIG. 8.
(a) Schematic representation of focussing and trapping of DNA using a device containing quadrapole electrodes. Initially DNA molecules (blue) are prefocused by converging streams generated by ACEO vortices and then undergo head-on collision to trap DNA at the center of the system, with the assistance of dipole-induced association between focused DNA and the holding of the trapped spot by the downward DEP force (pink). Reprinted with permission from Du et al., Biomicrofluidics 2(4), 044103 (2008). Copyright 2008 AIP Publishing LLC. (b) Rapid dielectrophoresis induced assay to trap ssDNA in a cusp-shaped nanocolloidal assembly. The microfluidic platform traps ssDNA in a nanocolloidal assembly functionalized with a capture probe under a locally amplified gradient field. The DNA molecule rapidly concentrates under optimal frequency, and the hybridized DNA is detected using a fluorescence detector. Reprinted with permission from Cheng et al., Lab Chip 10(7), 828–831 (2010). Copyright 2010 The Royal Society of Chemistry. (c) AC field induced DNA transport to capture DNA molecules on oligo functionalized CNTs. CNTs are trapped by dielectrophoresis by an AC field supplied by interdigitated electrodes (IDE). Sample containing target DNA is passed through the trapped DNA and detected using the observed change in impedance. Reprinted with permission from Basuray et al., ACS Nano 3(7), 1823–1830 (2009). Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society.