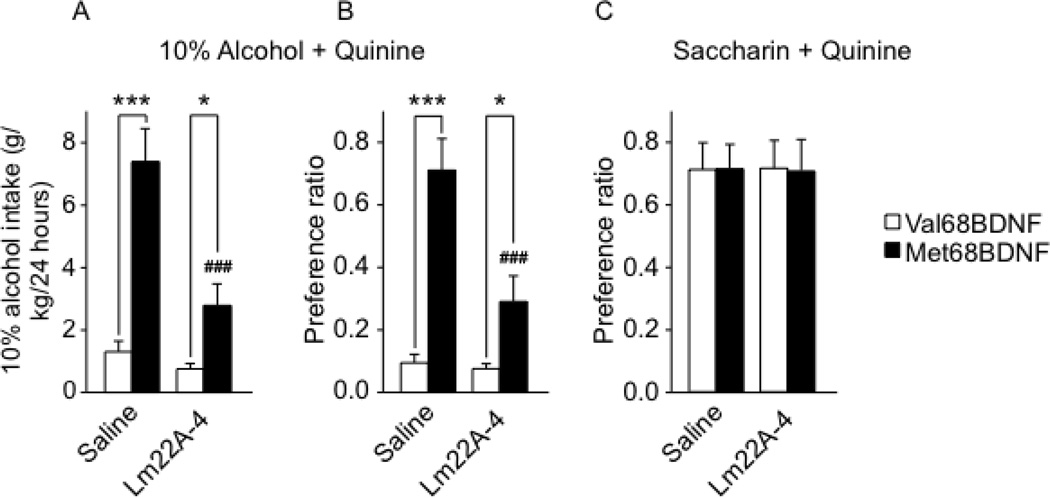
Figure 7. Activating the TrkB signaling pathway reduces consumption of quinine-adulterated alcohol by Met68BDNF mice.
Mice undergoing an intermittent access (2-bottle choice) to 10% alcohol/0.10 g/l quinine solution (see Supplementary Figure S12 A–B for basal level of alcohol drinking with or without quinine and Supplementary Fig. S12 C–D for basal level of saccharin drinking with our without quinine) received i.p. administration of 100 mg/kg LM22A-4 or saline immediately before the beginning of the drinking session. Intake of alcohol (g/kg/24 hrs) (A) or saccharin (ml/kg/24 hrs) (C). Preference for the alcohol+quinine (B) or saccharin+quinine (D) solution. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; ###P < 0.001 compared to Met68BDNF mice receiving saline, *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001; LSD post hoc test; (A–B) n=8 per genotype, (C) n=7 per genotype.