Figure 3.
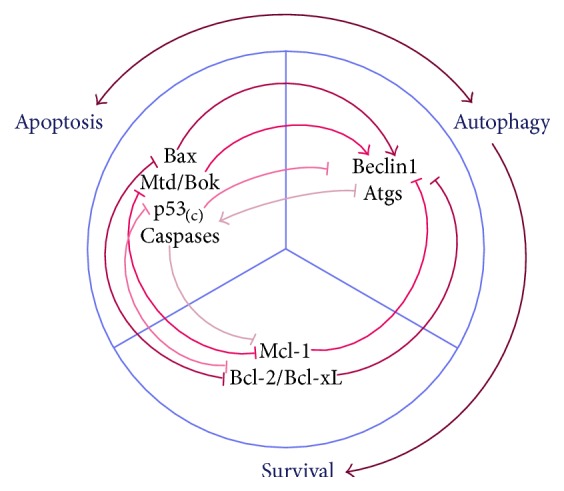
Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Many lines of evidence have proven the antiautophagic role of apoptosis. Cytoplasmic p53 inhibits the translation and activation of Atgs, and apoptotic caspases cleave Atgs to render them nonfunctional [97, 98]. However, proapoptotic BH3-only proteins like Bax disrupt the antiautophagic role of Bcl-2/Bcl-xL, resulting in induction of autophagy [64, 101]. Similarly, proapoptotic Mtd/Bok is a powerful autophagy inducer by countering the antiautophagic role of Mcl-1 [103]. Autophagy is thought to be a prosurvival function, but overactivated autophagy accelerates apoptosis by excessively degrading cellular substances [66]. Moreover, Atgs are also said to provide the platform for activation of caspases [100]. In a state of OS, apoptosis and autophagy may occur simultaneously. They may be stimulated separately by OS and at the same time be induced by each other. Thus, their relationship may influence cell fate and lead to different pathophysiological outcomes.
