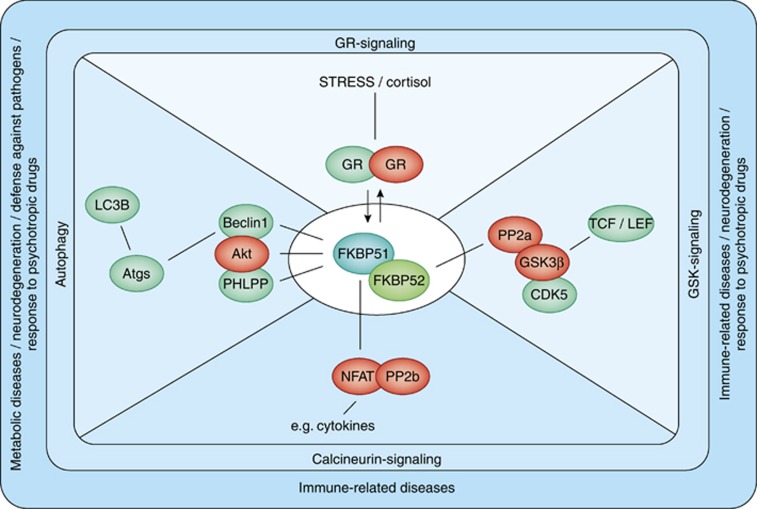
Figure 2.
Selected interactions of FKBP51/FKBP5 and their impact on molecular processes. As discussed in the text, FKBP51 exerts an inhibitory effect on GR function, thus having a crucial role in stress physiology. FKBP51 further interacts with PHLPP, Akt, and Beclin1 and affects Akt/Beclin1-driven autophagy. As PHLPP dephosphorylates Akt at serine 473, inactive Akt is recruited to Beclin1, resulting in lower inhibitory phosphorylation of Beclin1 and thus the induction of autophagic pathways. Impact on autophagy might be a link of FKBP51 with diseases characterized by defective autophagy, including neurodegeneration, inflammatory diseases, and aging. FKBP51 further interacts with CDK5 and PP2A resulting in inhibition of GSK3β and activation of promoters targeted by the transcription factors TCF/LEF. FKBP51 shows high affinity to calcineurin (PP2b), and high levels of FKBP51 result in inhibition of PP2b-directed NFAT-signaling, thus affecting T-cell proliferation and function. Green color represents activation and red color represents inhibition by FKBP51.