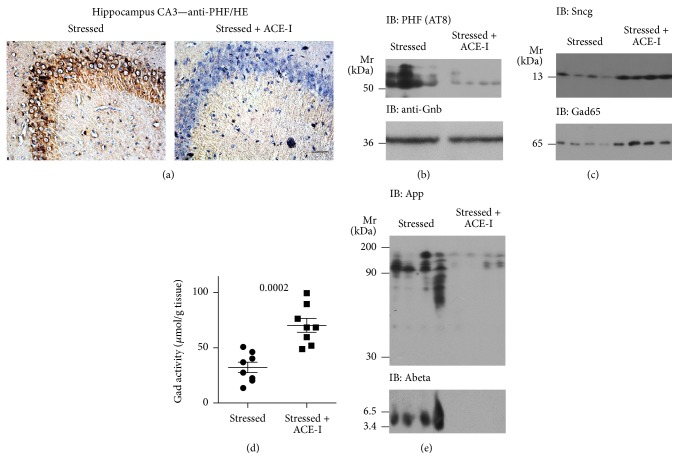
Figure 4.
Treatment with the brain-penetrating ACE inhibitor captopril retarded signs of neurodegeneration induced by chronic mild stress. (a) Immunohistological detection of hyperphosphorylated tau protein with anti-PHF antibody in hippocampal CA3 neurons of a stressed rat without treatment (left panel) relative to a stressed rat treated with the ACE inhibitor captopril (Stressed + ACE-I) during the stress protocol (right panel); bar: 40 μm. Immunohistological experiments are representative of 4 rats/group. (b) Immunoblot detection of hyperphosphorylated tau protein (IB: PHF (AT8)) in hippocampal extracts of stressed rats without treatment relative to stressed rats treated with the ACE inhibitor captopril (Stressed + ACE-I) during the stress protocol (n = 4/group). (c) Immunoblot detection of Sncg (upper panel) and Gad65 (lower panel) in hippocampal extracts of stressed rats without treatment relative to stressed rats with ACE inhibitor (Stressed + ACE-I) treatment (n = 4/group). (d) Hippocampal Gad activity of stressed rats without treatment relative to stressed rats treated with the ACE inhibitor (Stressed + ACE-I) captopril (n = 8/group; P = 0.0002). (e) Immunoblot detection of the amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein, App (IB: App; upper panel), and β-amyloid (IB: Abeta; lower panel) in hippocampal extracts of stressed rats without treatment relative to stressed rats treated with the ACE inhibitor captopril (Stressed + ACE-I) during the stress protocol (n = 4/group).