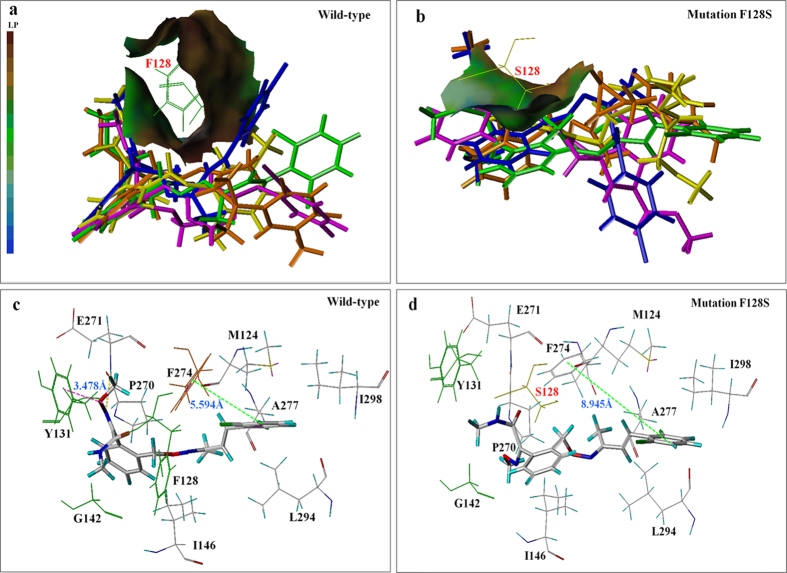
Figure 4. Docking interactions of the wild-type Qo pocket and the mutant type (F128S) Qo pocket with QoI fungicides.
(a) Indicates QoI fungicides are bond to a highly hydrophobic surface of Qo pocket including F128 (brown molecular surface). LP indicates the lipophilic potential; as the color of the molecular surface becomes browner, the surface is more lipophilic and more hydrophobic, but as the color becomes bluer, the surface becomes more hydrophilic and less hydrophobic. The fungicides (and color codes) are: azoxystrobin (magenta), SYP-1620 (green), ZJ0712 (yellow), SYP-2815 (orange), and enestroburin (blue). (b) Indicates QoI fungicides are bond to a less hydrophobic surface of Qo pocket (less brown molecular surface) when F is substituted by S at position 128. (c) 3D representation of SYP-1620 with the amino acid residues forming the wild-type Qo-binding pocket, and hydrogen bond (yellow dashes), π-interaction (magenta dashes) and π-π stacking (green dashes) were shown. (d) 3D representation of SYP-1620 with the amino acid residues forming Qo-binding pocket with the F128S mutation, π-π stacking almost disappeared when the distance between the side-chain of fungicides and the aromatic ring of F274 increased to 8.945 Å (green dashes).