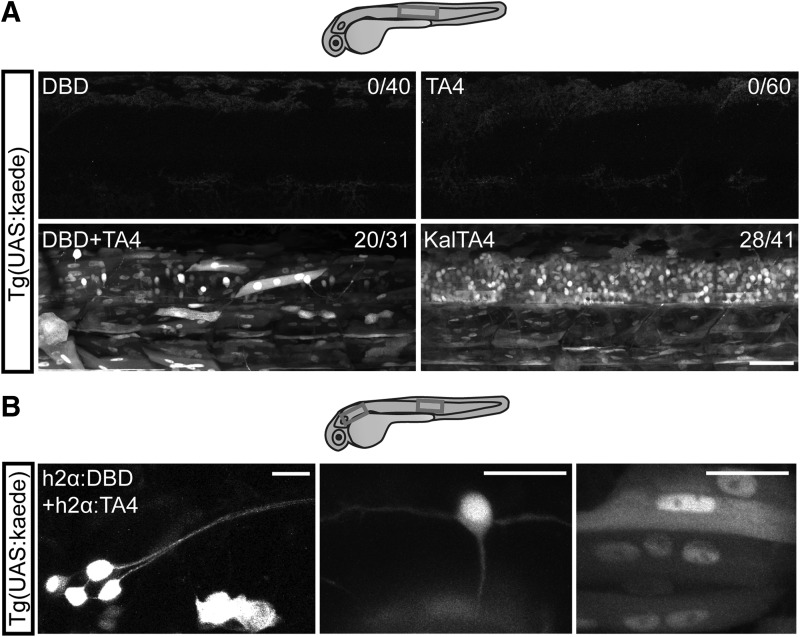
FIG. 2.
Split KalTA4 hemi-drivers reconstitute functional KalTA4 in several cell types. (A) Lateral view of the trunk region of 2 dpf Tg(UAS:kaede) larvae injected with split KalTA4 hemi-driver mRNA or control KalTA4 mRNA. Either DBD or TA4 mRNA alone does not activate kaede expression. DBD and TA4 mRNA in combination, or intact KalTA4 mRNA, is sufficient to activate the reporter UAS:kaede. Since heterozygous parent UAS:kaede fish were outcrossed, the subset of nonfluorescent embryos are likely nontransgenic offspring. Numbers on top right indicate number of kaede+ embryos/number of total embryos. Boxes indicate approximate imaged regions. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Lateral view of the pLL ganglion (left) or trunk region (middle and right) of 2 dpf Tg(UAS:kaede) larvae injected with h2α:DBD and h2α:TA4. h2α-driven split KalTA4 expression results in activation of the reporter UAS:kaede in a variety of cell types, including peripheral neurons in the pLL ganglion (left), central neurons in the spinal cord such as a commissural primary ascending interneuron (middle) and muscle cells (right). Boxes indicate areas of imaged cells. Scale bars: 20 μm. pLL, posterior lateral line.