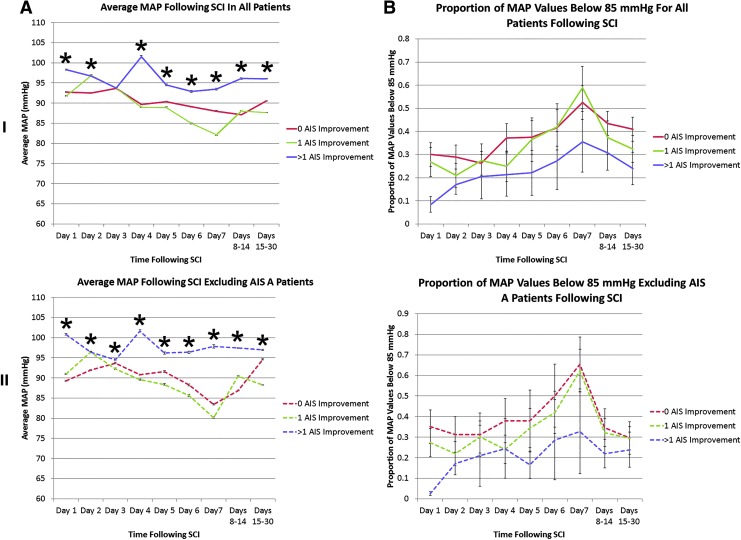
FIG. 2.
Average mean arterial pressure (MAP) and proportion of values <85 mm Hg are associated with outcome early after spinal cord injury in a noncumulative analysis. In (A), average MAP values are plotted in relation to time subsequent to intensive care unit admission. Values were measured with an arterial line. In (B), the proportion of MAP values below the lower limit of the recommended blood pressure range (85 mm Hg) are plotted. In (I), all patients with outcome data are plotted, while in (II), patients known to be American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale (AIS) grade A at final neurological examination are excluded. The latter case is denoted with dashed lines. For (A), the “n” used in statistical testing was the number of blood pressure measures, while in (B), it was the number of patients.
SCI, spinal cord injury.
*Denotes significance on analysis of variance performed at each time point. Error bars represent standard error.
I: For the group with 0 AIS grade improvement, n=35 patients; the group with 1 AIS grade improvement, n=23 patients, and the group with >1 AIS grade improvement, n=13 patients.
II: For the group with 0 AIS grade improvement, n=13 patients; the group with 1 AIS grade improvement, n=21 patients. and the group with >1 AIS grade improvement, n=10 patients. Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu