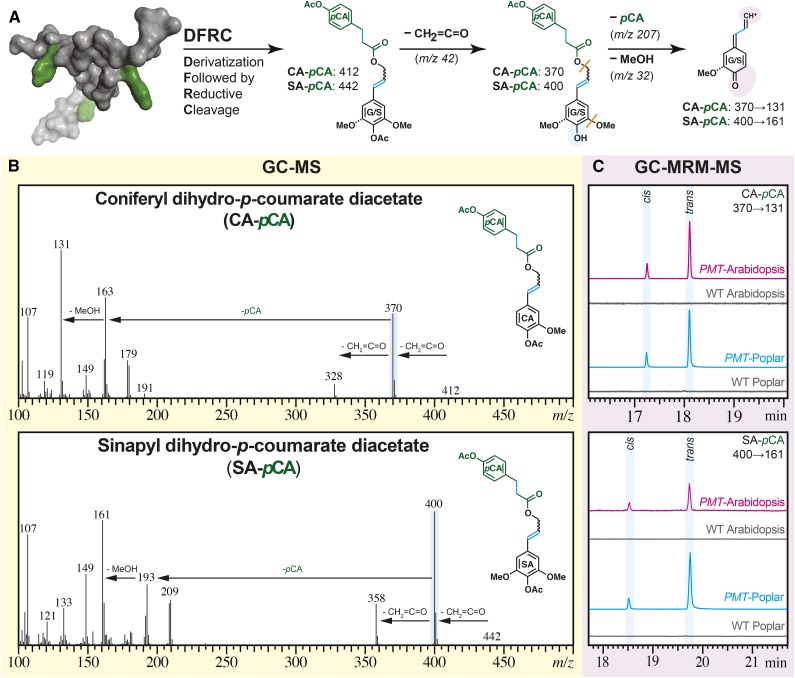
Figure 4.
MS evidence for the incorporation of ML-pCA conjugates into transgenic PMT Arabidopsis and PMT poplar. A, The DFRC assay releases a fraction of the pCA as diagnostic ML-pCA-derived structural signatures as indicated with cyan shading; both CA-DHpCA (generally just denoted as CA-pCA here) and SA-DHpCA (SA-pCA) are evidenced. The shaded ovals highlight the structural changes caused by electron ionization (blue) and MRM fragmentation (purple). The orange lines indicate bonds that cleave during the MRM transitions to the detected fragment. B, The mass spectra for synthetic model compounds CA-pCA and SA-pCA from a Q3 scan on a GC-triple-quadrupole MS: molecular ion (mass-to-charge ratio [m/z] = 412 and 442) loss of ketene (m/z = 42) to yield the base peak (m/z = 370 and 400). C, A stacked plot of the triple-quadrupole MRM chromatograms of DFRC-derived parent ions (m/z = 370 and 400) to one of the diagnostic product ions (m/z = 131) from WCW of PMT Arabidopsis (magenta), wild-type (WT) Arabidopsis (gray), PMT poplar (cyan), and wild-type poplar (gray).