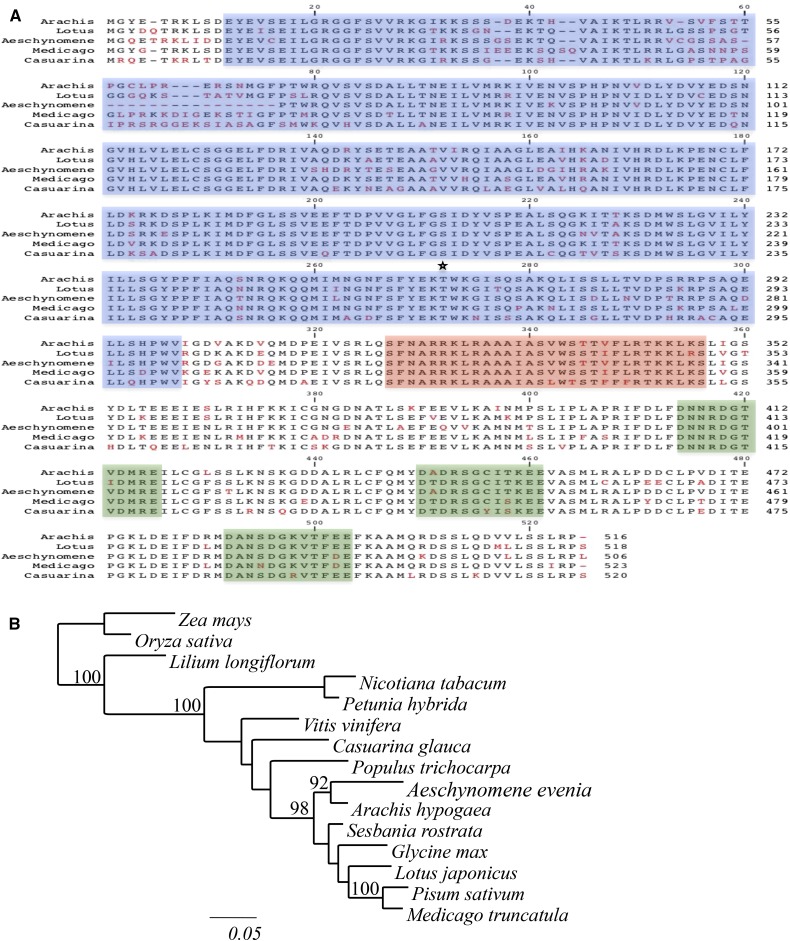
Figure 1.
Features of the CCaMK of A. evenia. A, Alignment of CCaMK from A. evenia, Arachis hypogea, L. japonicus, M. truncatula, and C. glauca. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW. Identical amino acids are in black, and different amino acids are in red. On the basis of in silico predictions, catalytic domain, calmodulin-binding domain, and EF-hands of the visinin-like domain are highlighted in blue, red, and green, respectively, and the autophosphorylation site is indicated by the star. B, Position of A. evenia CCaMK in a distance tree predicted based on available CCaMK protein sequences. The tree was generated based on a Clustal Omega alignment of 474 amino acids. Numbers at the nodes represent bootstrap values (percentage of 100 replicates; only values greater than 90% were retained). Accession numbers of the proteins are as follows: NP_001105906.1 (Zea mays), NP_001055895.1 (Oryza sativa), Q43531.1 (Lilium longiflorum), AAD52092.1 (Nicotiana tabacum), ABQ95545.1 (Petunia hybrida), XP_002273342.1 (Vitis vinifera), CCW43374.1 (C. glauca), XP_002315401.2 (Populus trichocarpa), ACB46142.1 (A. hypogaea), ACC94267.1 (Sesbania rostrata), XP_003531786.1 (Glycine max), A0AAR7.1 (L. japonicus), Q6RET6.2 (Pisum sativum), and XP_003628124.1 (M. truncatula).