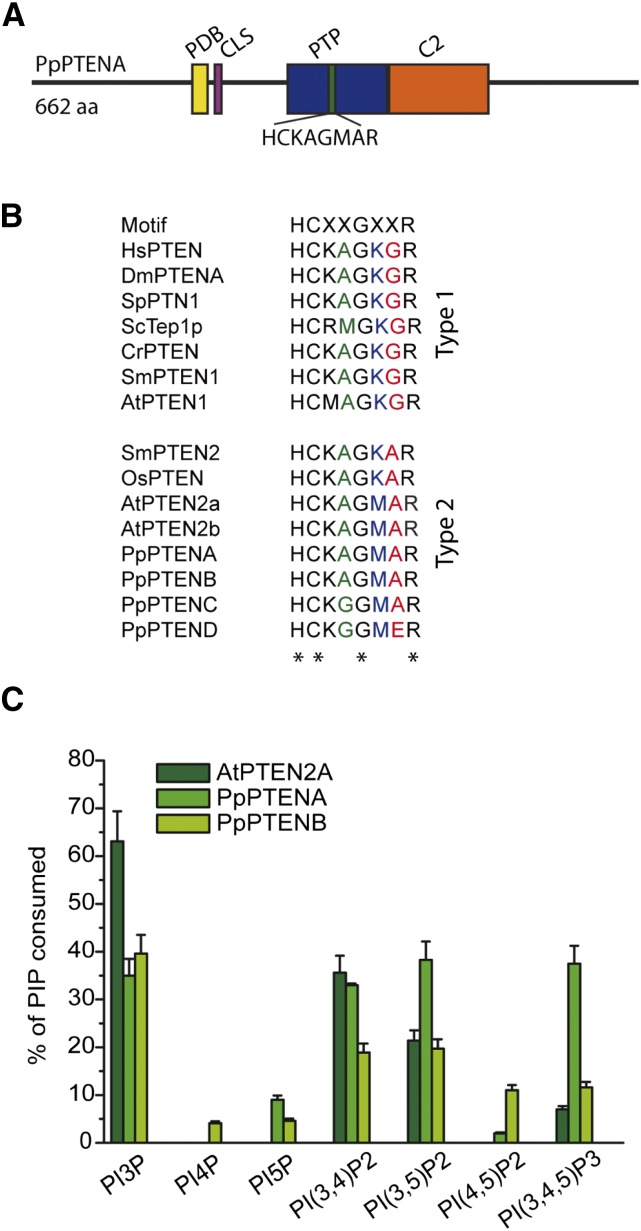
Figure 1.
Modular and biochemical characterization of P. patens class II PTENs. A, Modular structure of PpPTEN proteins. PtdIns(4,5)P2-binding domain (PBD), cytosolic signal (CLS), phosphatase domain (PTP), and C2 domain (C2). B, PTEN phosphatase signature motif HCXXGXXR (phosphate-binding loop) responsible for the hydrolysis of PPIs. In HsPTEN the sequence corresponding to this phosphatase signature motif is HCKAGKGR (comprising residues 123–130). C, Biochemical characterization of PPI phosphatase activity of recombinant GST-AtPTEN2a and GST-PpPTENs and GST proteins. The activity was measured by the amount of free inorganic phosphate released from the substrate using a malachite green assay. Reactions were performed in triplicates, and results are represented by bars as the mean ± sd. PI4P, Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate; PI5P, phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate; PI(3,4)P2, phosphatidylinositol-(3,4)-bisphosphate; PI(3,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol-(3,5)-bisphosphate; PI(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate; PI(3,4,5)P3, phosphatidylinositol-(3,4,5)-trisphosphate; ScTep1p, tensin-like phosphatase; WT, wild type.