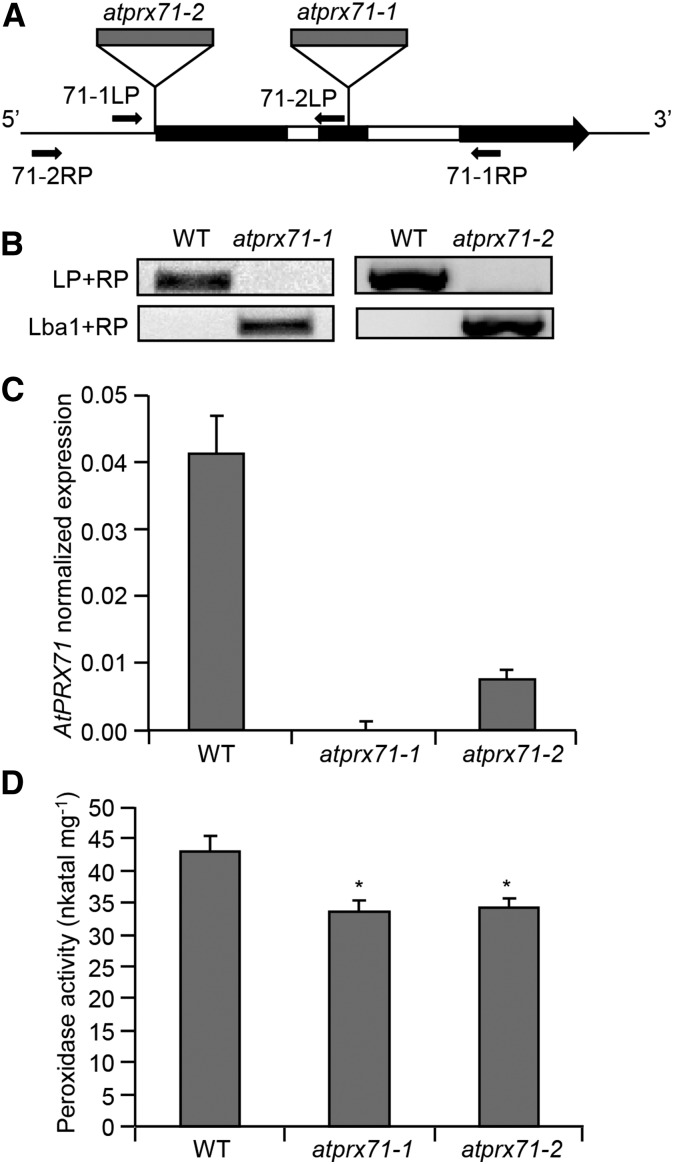
Figure 2.
Isolation of insertional mutants for AtPRX71. A, Schematic representation of the AtPRX71 locus. Exons and introns are represented in black and white, respectively. Localization of T-DNA insertions (gray) and the primers used for genotyping of atprx71-1 and atprx71-2 are shown. B, Genotyping of atprx71-1 and atprx71-2. Genomic DNA from the wild type (WT) and mutants was subjected to PCR using primer pairs for the wild-type allele (LP + RP) or the T-DNA insertion (Lba1 + RP). LP, 71-1LP or 71-2LP; RP, 71-1RP or 71-2RP. C, Expression of AtPRX71 was analyzed in wild-type, atprx71-1, and atprx71-2 rosette leaves by qPCR using UBQ5 as the reference gene. Bars represent average arbitrary units ± sd of three technical replicates. This experiment was repeated twice with similar results. D, Total peroxidase activity in protein extracts from wild-type, atprx71-1, and atprx71-2 10-d-old seedlings was determined by a guaiacol oxidation-based assay. Bars represent average activity ± se of at least six independent samples. This experiment was repeated twice with similar results. *, Statistically significant differences between the wild type and mutants according to Student’s t test (P < 0.05).