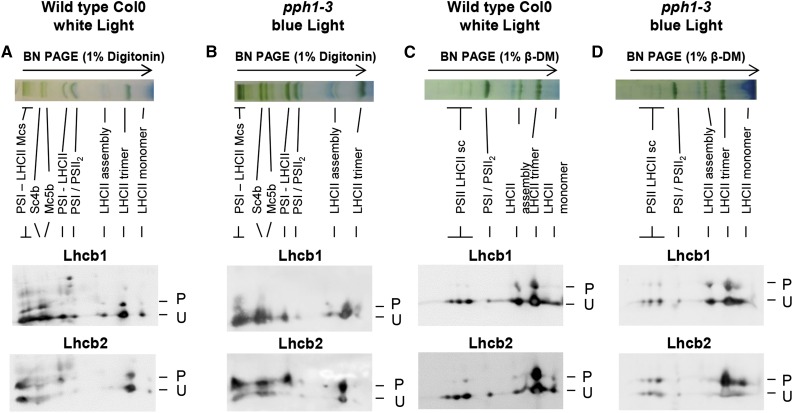
Figure 4.
Lhcb1 and Lhcb2 phosphorylation in different supercomplexes. Wild-type Col0 (ecotype Columbia 0) plants were grown under white light (70 μmol sec−1 m−2) and harvested 4 h after the onset of light. Thylakoid membranes were solubilized and subjected to BN-PAGE in the first dimension (top). The lanes were then subjected to a second dimension of two-layer Phos-tag PAGE and immunoblotting to reveal the phosphorylation of Lhcb1 and Lhcb2 (P, phosphorylated; U, unphosphorylated). A, Col0 wild-type plants were grown in white light. Thylakoid membranes were solubilized with digitonin. B, Mutant pph1-3 plants were treated with far-red light (1 h) and then blue light (30 min) to increase antenna phosphorylation. Thylakoid membranes were solubilized with digitonin. C, Col0 plants were grown in white light as in A, and thylakoid membranes were solubilized with β-DM. D, Mutant pph1-3 were treated as in B, and thylakoid membranes were solubilized with β-DM. The bands are labeled as described by Järvi et al. (2011): Mcs, megacomplexes; Sc4b, supercomplex 4b; Mc5b, megacomplex 5b; PSI-LHCII, STN7-dependent PSI-LHCI-LHCII supercomplex; PSI/PSII2, comigrating PSI-LHCI and PSII dimer; LHCII assembly, LHCII complex containing an LHCII trimer associated with monomeric Lhcbs (mainly Lhcb4 and Lhcb6); and PSII LHCII sc, PSII dimer-LHCII supercomplexes.