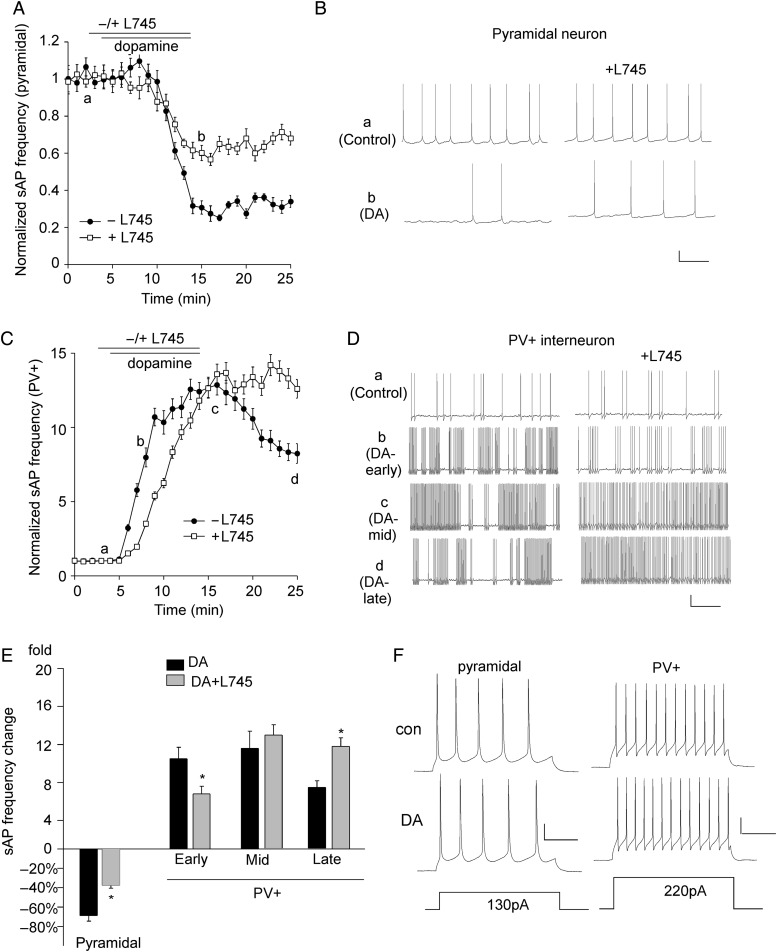
Figure 7.
The effects of dopamine on sAP in PFC pyramidal neurons and PV+ interneurons are partially mediated by D4 receptors. (A) The time course of normalized sAP frequency showing the effect of dopamine (1 μm) in the absence (control) or presence of the D4 antagonist L745870 (20 μm) in PFC pyramidal neurons. (B) Representative traces of sAPs at different time points (denoted by a,b) in plot A. Scale bars: 20 mV, 1 s. (C) The time course of normalized sAP frequency showing the effect of dopamine (1 μm) in the absence (control) or presence of L745870 (20 μm) in PFC PV+ interneurons. (D) Representative traces of sAP at different time points (denoted by a–d) in plot C. Scale bars: 20 mV, 1 s. (E) Bar graph summary of the change in sAP frequency by dopamine in the absence or presence of L745870 in PFC pyramidal neurons and PV+ interneurons. The time-dependent effects of dopamine were analyzed in early (b), mid (c), and late (d) stages. *P < 0.05. (F) Representative traces of action potentials evoked by injected currents (20 s/pulse) before and after dopamine (1 μm) application in a PFC pyramidal neuron and a PV+ interneuron. Scale bars: 20 mV, 100 ms.