Figure 1.
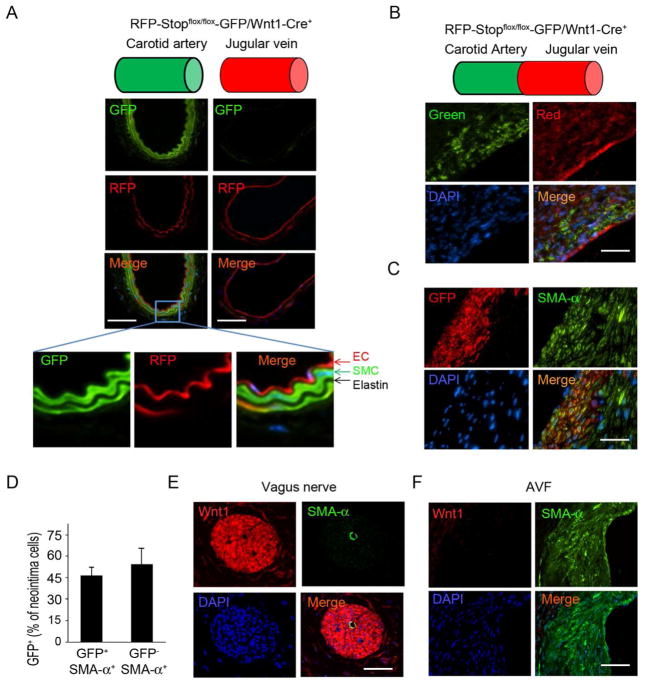
SMCs from the anastomosed artery contribute to neointima formation in AVFs. A. Wnt1-Cre-mediated GFP expression in SMCs of the common carotid artery in RFP-Stopflox/flox-GFP/Wnt1-Cre+ mice. Frozen sections of arteries or jugular veins were assessed by fluorescent microscopy (EC, endothelial cell). B. AVFs were created in RFP-Stopflox/flox-GFP/Wnt1-Cre+ mice and the frozen sections were prepared to detect fluorescent signals without immunostaining. The positive signals were recorded under green and red channels. C. AVFs were created in RFP-Stopflox/flox-GFP/Wnt1-Cre+ mice and collected in paraffin section (this treatment eliminated fluorescent signals), and GFP-positive cells incorporated into the neointima were detected using immunostaining with anti-GFP (red) or SMA-α-FITC antibodies (green). D. Statistical analysis of GFP positive cells in total of SMA-α positive neointima cells. Total 5 slides from each AVF sample were counted under 400 X view (n = 4). E & F. Wnt1 expression was examined by immunofluorescent staining in vagus nerve (E) and in AVFs (F). (Scale: 50 μm; n = 4).