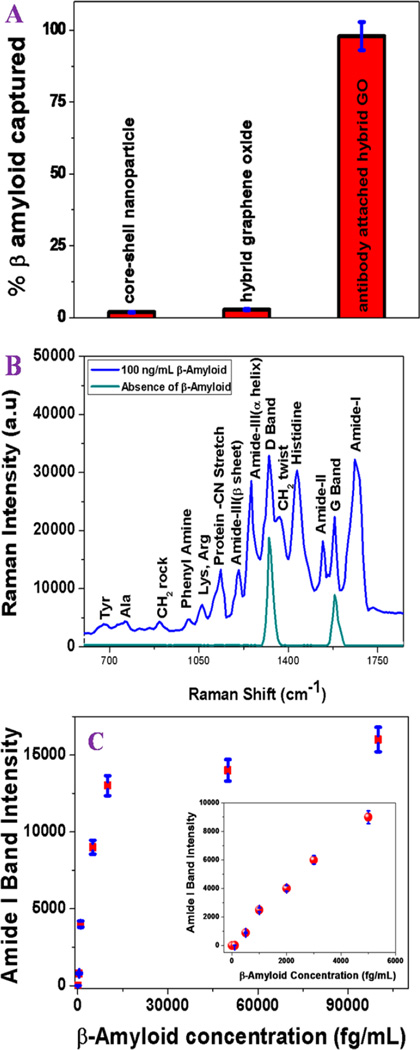
Figure 2.
(A) ELISA results showing β amyloid capture efficiency from infected blood samples using anti-β amyloid antibody attached plasmonic-magnetic hybrid graphene oxide based nanoplatform. Plots also show that separation efficiency is less than 3% in the absence of anti-β amyloid antibody. (B) Spectrum showing SERS intensity from β amyloid conjugated nanoplatform after magnetic separation. Observed SERS signal is directly from the β amyloid. Other than D and G bands, no SERS signal was observed when whole blood without β amyloid was used. (C) Plot showing how SERS amide I band intensity from β amyloid conjugated nanoplatform changes with concentration between 0 and 6 pg/mL. Our experimental data show that the detection efficiency can be as low as 500 fg/mL.