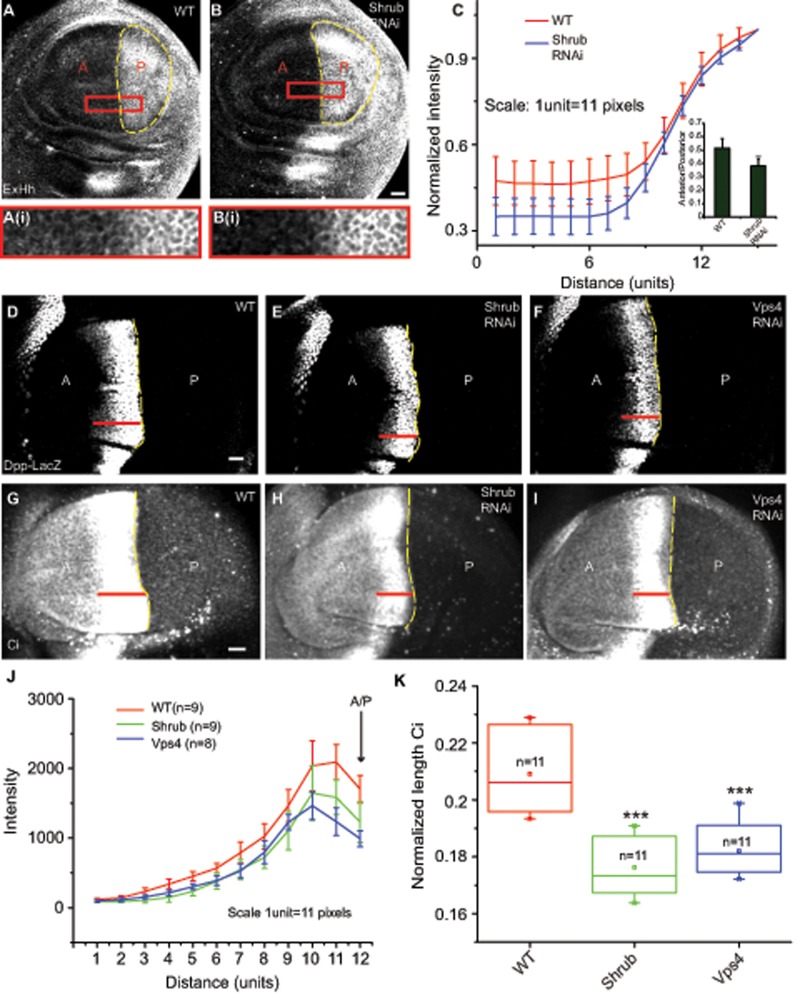
FIGURE 7:
Perturbations of Shrub and Vps4 proteins affect Hh spread and its signaling output in the wing imaginal disc. (A, B) Drosophila wing imaginal discs stained for extracellular Hh (ExHh) from WT (A) and animals expressing Shrub (B) RNAi under the control of Hh-Gal4, marked using the yellow dashed lines, show a reduction in spread of Hh in the anterior domain in RNAi-treated discs. Images were subjected to median filtering before representation. Scale bar, 20 μm. Outlined regions are shown at a higher magnification. (C) Quantification shows a reduction in the spread of extracellular Hh in Shrub RNAi–treated discs compared with the WT control. The line represents an averaged trace from seven wing imaginal discs in each condition. Graph in the inset shows a reduction in anterior/posterior ratio of Hh intensities in Shrub RNAi. Data are represented as mean ± SD from seven wing imaginal discs for each condition; **p < 0.01. (D–I) Drosophila wing imaginal discs from WT (D, G) or expressing Shrub RNAi (E, H) or Vps4 RNAi (F, I) under the control of Hh-Gal4 and stained for Dpp-LacZ (D–F) or Ci (G–I) and imaged using FV1000 confocal microscope. Red lines indicate the extent of staining seen in each of the representative discs. Scale bar, 20 μm. (J) The traces (mean ± SD) indicate the distribution of Dpp-LacZ intensities along the A/P axis into the anterior obtained from the indicated number of wing imaginal discs for each treatment. A significant reduction in both intensities, as well as in spread, is seen in both Shrub and Vps4 RNAi conditions. (K) Box plot shows the median and the range of data obtained from the indicated number of discs of normalized length of the staining domain (average length of the stripe/length of the wing imaginal disc along the dorsoventral axis) of Ci under different conditions; ***p < 0.001.