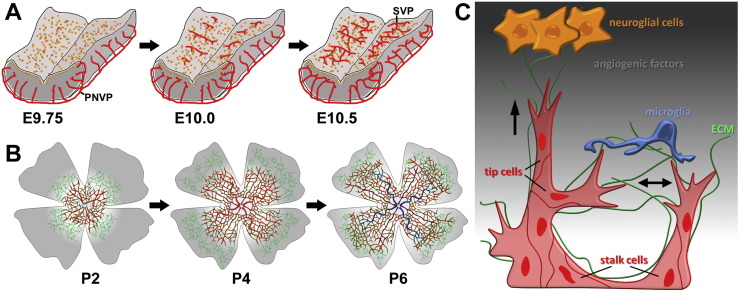
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of CNS vascularisation. (A,B) Time course of blood vessel growth in the mouse embryo hindbrain (A) and postnatal retina (B). Neural progenitors are shown in orange, the non-remodelled vascular plexus in red, arteries in dark red and veins in blue; fibronectin-expressing astrocyte networks are shown in green. (C) Mechanisms of blood vessel growth in the CNS. Hypoxic neuroglial cells (orange) secrete angiogenic factors and extracellular matrix (ECM), indicated by a grey background gradient and as green strands, respectively. During angiogenesis, endothelial cells (red) undergo tip cell/stalk cell specialisation; tip cell convergence for vascular circuit formation is assisted by yolk sac-derived CNS tissue macrophages, also called microglia (blue). Arrows indicate the direction of tip cell migration. PNVP, perineural vascular plexus; SVP, subventricular vascular plexus; a, artery; v, vein.