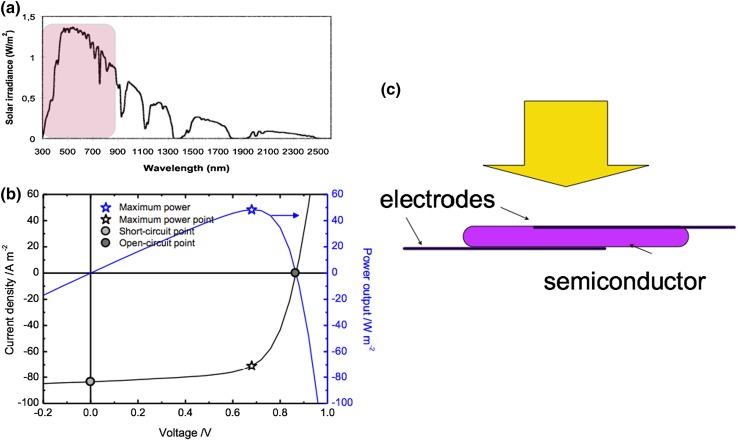
Fig. 2.
a The solar radiation arriving at the surface of the earth is distributed over different wavelengths of light, with tails extending far out in the infrared and invisible region. With semiconductor materials, light with energy higher/wavelengths shorter than the band gap of the material can be absorbed (shadow in graph), but none below the band gap. b The semiconductor is contacted with electrodes and exposed to solar light. Photocurrent J sc from the devices depends on absorption and charge generation in the active material; the photo-voltage V oc basically depends on the materials. c The current–voltage curve shows both these parameters, and the device is used to deliver electricity at the maximum power delivery point, indicated with a star