Table 1.
Optimization studies. 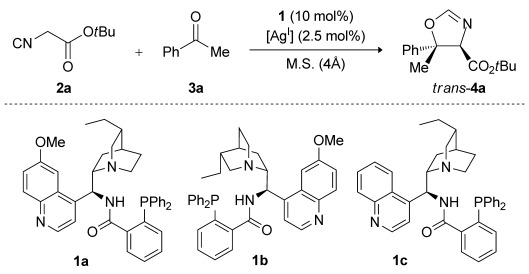
| Entry | 1 | [Ag] | T[°C] | Solvent | t[h] | Yield[a] [%] | d.r.[b] | e.r.[c] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 c | Ag2O | −20 | EtOAc | 60 | 78 | 89:11 | 90:10 |
| 2 | 1 a | Ag2O | −20 | EtOAc | 60 | 93 | 95:5 | 94:6 |
| 3 | 1 b | Ag2O | −20 | EtOAc | 60 | 82 | 90:10 | 90:10[d] |
| 4 | 1 a | Ag2CO3 | −20 | EtOAc | 24 | 64 | 91:9 | 94:6 |
| 5 | 1 a | AgOAc | −20 | EtOAc | 48 | 55 | 88:12 | 91:9 |
| 6 | 1 a | Ag2O | −20 | TBME | 36 | 74 | 88:12 | 94:6 |
| 7 | 1 a | Ag2O | −20 | CH2Cl2 | 36 | 63 | 79:12 | 85:15 |
| 8 | 1 a | Ag2O | −20 | iPrOAc | 36 | 79 | 89:11 | 93:7 |
| 9 | 1 a | Ag2O | −30 | EtOAc | 96 | 84 | 90:10 | 94:6 |
| 10 | 1 a | Ag2O | 0 | EtOAc | 48 | 84 | 89:11 | 92:8 |
| 11 | 1 a | – | −20 | EtOAc | 120 | 0 | – | – |
| 12 | – | Ag2O | −20 | EtOAc | 120 | 0 | – | – |
Combined yield of both diastereomers after flash column chromatography.
The diastereomeric ratio (d.r.) is given as the trans/cis ratio and was determined by 1HNMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture.
The enantiomeric ratios (e.r.) were determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase.
Enantiomeric (4S,5R)-4 a was obtained. M.S.=molecular sieves, TMBE=tert-butyl methyl ether.
