Fig. 5.
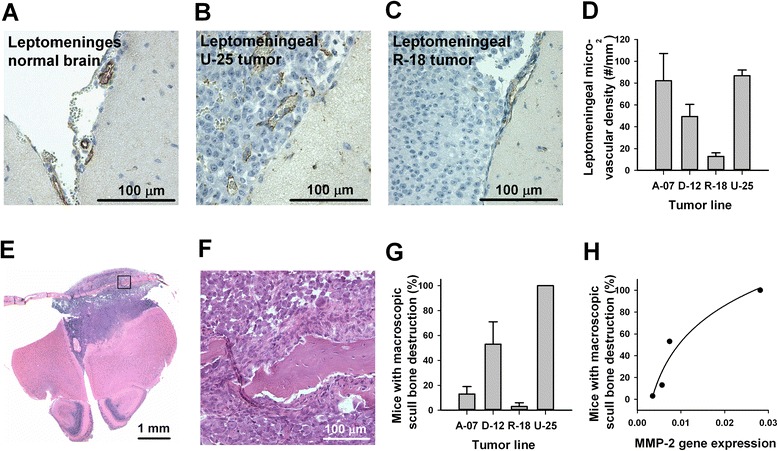
Intertumor heterogeneity in meningeal vascularization and scull bone invasion. a–c Histological brain sections stained for CD31 to visualize blood vessels in the leptomeninges of a normal brain (a), a leptomeningeal U-25 tumor (b), and a leptomeningeal R-18 tumor (c). d Microvascular density in leptomeningeal tumors assessed from CD31 immunohistochemistry. Columns and bars represent mean and SEM of 4 mice. e HE-stained coronal section through the brain and overlying scull bone ~1 mm anterior to the site of intracerebral injection of U-25 cells. f High magnification image of area indicated in E showing scull bone disrupted by tumor growth. g Fraction of mice with macroscopic scull bone destruction at autopsy. Columns and bars represent mean and SEM of three separate experiments, each involving 10 mice. h Fraction of mice with macroscopic scull bone destruction versus MMP-2 gene expression assessed by quantitative PCR. Points represent melanoma cell lines. Line represents logarithmic regression curve (y = y0 + a · ln x, R 2 = 0.93, P < 0.05)
