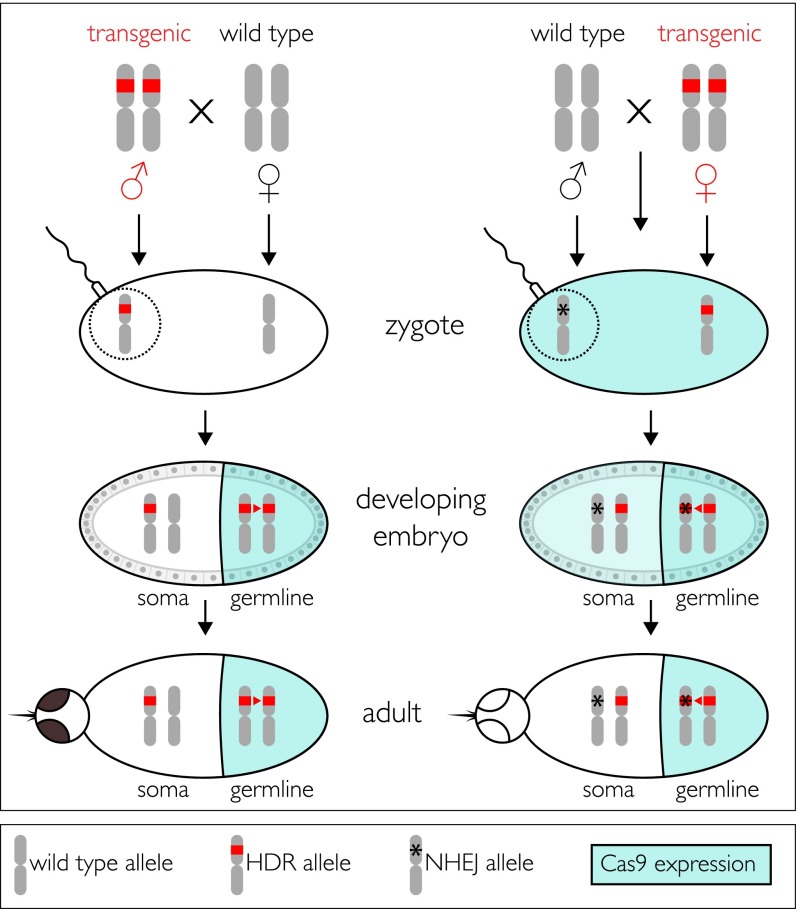
Fig. 5.
Model of AsMCRkh2 transgene activity in adult males and females. (Top) Schematic representations of the third chromosomes of An. stephensi. Transgenic males (Left) and females (Right) are depicted as being homozygous in the germline for AsMCRkh2 (red bars) and are outcrossed to wild-type mosquitoes of the opposite sex. Zygotes resulting from outcrosses of transgenic males do not have the Cas9 nuclease in the eggs (clear oval), which are derived from wild-type females, and somatic cells remain heterozygous for the AsMCRkh2 transgene. A schematic representation of the sperm attached to the egg and the donated paternal chromosome is represented encircled by the dotted line. vasa-mediated expression of Cas9 is restricted to the germ line (colored half-oval) in developing embryos derived from transgenic AsMCRkh2 males, resulting in significant HDR (red arrowhead) that converts the majority of the chromosomes by insertion of the AsMCRkh2 cargo. Adults are phenotypically positive for the dominant reporter gene, DsRed, and wild-type in eye color. In contrast, zygotes resulting from outcrosses of transgenic females have Cas9 nuclease in the eggs (aqua-colored oval) as a result of vasa-directed expression in the maternal germ line, and this catalyzes nonhomologous end joining (asterisk) to mutate the paternally derived wild-type chromosome (encircled by the dotted line). Some HDR may occur at this stage, but may be hampered by an initial physical separation of the maternal and paternal chromosomes. Embryos derived from transgenic AsMCRkh2 females also have vasa-mediated Cas9 expression restricted to the germ line (colored half-oval), but in addition have the nuclease perduring from the maternal gamete (light-colored half-oval), which can result in adults that are phenotypically positive for the dominant reporter gene, DsRed, and exhibit the white or mosaic eye color. Furthermore, the paternally derived chromosomes mutagenized in the zygotes are resistant to subsequent HDR and insertion of the cargo. Some of the male-derived chromosomes may not be mutagenized, and these can be substrates for HDR. Both options are shown as the asterisk overlying the red bar in the germ line.